Dry construction technologies help to quickly and easily build internal enclosing structures and create the basis for decorative ones. They are based on a metal frame and casing made of various sheet materials. Thanks to the small mass of parts, finished structures, such as interior partitions, are much lighter than those built from brick, concrete blocks, tongue-and-groove slabs.
In addition, the latter require subsequent plastering and other wet processes for final leveling of the surface. And the thicker the layer of plaster, the longer it takes to dry and the longer it takes before finishing begins. During dry construction, labor-intensive wet processes are minimized, which significantly reduces repair time.
Gypsum fiber and plasterboard sheets
The name of the sheets is associated with the materials from which they are made. Gypsum fiber gypsum board is a homogeneous, flat sheet containing gypsum reinforced with cellulose fiber. There are the following varieties: standard, which is used in rooms with low humidity, waterproof - for rooms with high humidity.
Gypsum fiber plasterboard is a homogeneous sheet, there are two types: regular and moisture resistant.
GKL - what is it: the decoding of this abbreviation means plasterboard sheet. This material consists of two layers: the middle is made of gypsum, the outer parts are made of cardboard. There are the following types:
- fire-resistant (GKLO) – coated with a fire-resistant composition;
- moisture-resistant (GKLV) – containing a substance that resists mold, fungi, and bacteria;
- combined (KGP PS) - with polystyrene foam composition for insulation, can be used for internal and external work;
- decorative – exclusive, requires careful installation.
Gypsum fiber
Cellulose fiber gives plasterboard sheets strength
This material appeared on our market much later than plasterboard sheets, but was already able to compete with its popular brother. The design of a gypsum fiber sheet, as in the design of gypsum boards, is based on the gypsum component.
However, the production technology of gypsum fiber boards differs from the production technology of gypsum boards. In this case, before pressing, gypsum is mixed with cellulose fiber, which plays the role of a reinforcing frame.
The surface of the gypsum fiber is not covered with cardboard, but is sanded and impregnated with water-repellent primers, which also prevent the formation of gypsum dust. The result is a multifunctional material that is not afraid of dampness and fire.
Pros of GVL
First of all, this material is good for its strength, which far exceeds the strength of drywall of similar thickness. The undeniable advantages also include the already mentioned moisture resistance and fire resistance. About the features of GVL, watch this video:
For rooms with particularly high humidity, for example, bathrooms, a special type of gypsum fiber with increased water-repellent properties is produced. In terms of its functionality, gypsum plasterboard is in no way inferior to plasterboard: it is used for the construction of partitions and wall cladding, for the creation of suspended ceiling structures and decorative interior structures.
Relevance of using gypsum boards
The material is used to create partitions, various structures, and wall cladding. GCR is easy to install, so you can implement various ideas in terms of interior design, achieve cosmetic cleanliness in your living space, and also implement original construction and finishing ideas even on your own.
USEFUL INFORMATION: How to choose wallpaper for the living room: interior design
Thanks to sheets of drywall, owners can easily:
- eliminate uneven surfaces in the apartment, hide corners or curved walls;
- make a redevelopment by installing partitions;
- create exquisite design structures in the form of arches, niches, columns;
- complement the room with built-in lighting.
Drywall instead of plaster - pros and cons
So, we have come to consider the strengths and weaknesses of this finishing material. Let's figure it out together.
Pros:
- Minimum dirt and debris. During the period of work, you will not find dirty or wet marks on the floor, since this material has a dry structure and does not require moisture at all.
- Ease of operation and installation. Anyone can level gypsum board walls without any special construction or carpentry skills. It will not be difficult to install drywall on the ceiling surface yourself.
- Possibility of waterproofing. Covering with such material allows you to cover the walls in order to create a waterproofing system that will save the room from noise coming from the street.
- The use of fire-resistant material will provide fire protection to the walls.
- Moisture absorption capacity. Thanks to this property, your walls will be able to “breathe”, so fungus does not form under the finish.
- Possibility of masking communications. Between the gypsum board sheets and the wall there will be an empty space in which cables and other types of communications can be hidden, and it can also be filled with insulation.
- Good flexibility. Plasterboard sheets bend well, which allows you to create various designs on walls and ceilings.
Flaws:
- Reducing usable area. The gypsum board needs to be mounted on a special metal sheathing, which will take up most of the space in the room.
- Carrying out several finishing works. Wall covering is just one stage of work, after which you need to putty the seams and apply a fixing finishing material.
- Inability of sheets to withstand heavy loads. A plasterboard wall cannot support a large and heavy shelf or bulky interior items, so additional elements are placed under the sheets.
Comparison results - which is better to choose?
Gypsum fiber panels differ from plasterboard in increased strength, durability, sound and heat insulation properties, as well as fire resistance. Therefore, it is the most preferred material for cladding walls and ceilings , subject to the availability of the necessary technical conditions. However, it will not allow the formation of surfaces of complex shapes.
Drywall is recommended for use when the budget for work is limited , in order to create structures with complex geometry, as well as when the load-bearing capacity of walls, ceilings or the entire facility is insufficient.
Which is better, gypsum plasterboard or gypsum plasterboard, if you look at the strength of materials? Gypsum fiber is preferable for rooms with higher requirements regarding impact protection. How important this is in relation to apartments is up to the owners to decide.
Drywall is easier to break through, its cardboard shell can be damaged, and it can “go limp” from moisture. Gypsum fiber is much stronger, you can hammer nails into it, it will not crumble.
Drywall or plaster - which is better to use?
Many new home owners are increasingly deciding to use plasterboard on interior walls instead of traditional plaster. This solution, however, has some disadvantages, although, without a doubt, this technology is much cheaper and allows you to quickly finish all walls.
From year to year, plasterboard is becoming an increasingly popular material in residential construction, repair and reconstruction. This is indeed a very good material for the walls of any room, including baths and kitchens, in addition, it can be used for false ceilings. But in order to make the right choice, you need to carefully analyze whether to level the walls with plasterboard or plaster and what will be better in each case.
Finishing walls with plaster - advantages
Plastering interior walls has many advantages:
For living rooms and living rooms, you should choose traditional gypsum or clay plaster. At the same time, such a choice will not be the best solution for premises where there is a high risk of damage to the walls - garages, workshops, etc. For such premises, stronger cement-lime mixtures are best suited.
The solution should be applied approximately 1-2cm thick. To secure the surface and ensure durability of the coating, the walls should be primed with special compounds. And only then apply one or two layers of plaster.
We advise you to study - What are the sizes of metal tile sheets and additional elements?
You can also perform machine plastering, which significantly speeds up finishing work.
Disadvantages of plaster
- The biggest disadvantage of this type of finishing is the need to thoroughly dry the walls before applying a decorative layer, such as paint or wallpaper. In order to ensure that the wall dries, you need to wait about 3 weeks. This increases repair time but provides a durable coating.
- Carrying out the work requires experience and high precision in applying the solution and leveling it in order to create a completely perfect wall, without “waves”. Special beacons for plaster make the process easier, but they will require additional costs.
In turn, the big advantage of plaster walls compared to plasterboard is that the plaster forms a dense surface over the entire wall, unlike gypsum boards. If the seams between the slabs are poorly finished, vertical and horizontal cracks may appear on the walls over time.
It is very easy to make grooves in a plastered wall for wires and cables, as well as plumbing pipes
This is important if it is necessary to reconstruct and install or add new cables
Gypsum fiber: how it differs from plasterboard
There are not so many main differences between plasterboard and gypsum fiber, or rather, only one. If plasterboard is made from pure gypsum, which is placed inside a cardboard shell, then in gypsum fiber boards, during production, cellulose fibers are added to the gypsum solution, which determine all the characteristics of this material.
The gypsum fiber board does not fit inside the cardboard shell. In fact, this combination of natural and artificial materials made it possible to create slabs that can be classified as both plasterboard and chipboard - something in between, combining all the advantages of both materials.
What to choose: gypsum fiber or drywall
Now about the properties and advantages that will allow you to decide what to choose: hypofibre or plasterboard. The advantages of this material include the following.
- High strength. If a sheet of plasterboard can be easily broken or even punched by hand, then with gypsum fiber such a number will not work. Cellulose fibers make these sheets so strong that they can even withstand the load of bulky and heavy furniture. Yes, yes, you heard right - one of the areas of application of gypsum fiber boards is the installation of floors using the dry method. This technology is also called dry screed - this is where gypsum fiber is used for the floor.
- Increased resistance to moisture. There are two types of gypsum fiber boards - regular and moisture resistant. If we compare moisture-resistant drywall with a similar gypsum fiber board, the latter is more resistant to moisture. It can remain in water for a long time and not swell - gypsum fiber in the bathroom can be called an ideal option for leveling walls, ceilings and even floors.
- Less susceptible to deformation than drywall. This point can be attributed to both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, this is good (the material is practically not subject to mechanical and other influences), but on the other hand, it is bad (gypsum fiber is not very suitable for making figured ceilings).
- A high degree of heat and sound insulation, which is achieved thanks to the same cellulose. If you use gypsum fiber to create interior partitions, then you can safely refuse the insulation that is placed in the cavity between the sheets.
- High fire safety. As you know, plasterboard belongs to the flammability group B2, and gypsum fiber to group B1 - it is practically not subject to combustion due to the absence of a cardboard shell.
If we talk about the disadvantages of this material, we can note several: firstly, it is higher in cost than plasterboard; and, secondly, the need for mandatory surface treatment with putty. In contrast, drywall only requires sealing the seams and screw heads.
Advantages and disadvantages of gypsum fiber
Panels with gypsum filler
All three types of panels are often identified as drywall, although this is not entirely correct, since they all have their own characteristics.
Each type of panel has its own main abbreviation, this is:
- GKL - plasterboard sheet.
- GVL - gypsum fiber sheet.
- GSP - gypsum particle board.
GKL
Table of differences between plasterboard sheets
| Abbreviation | View | General characteristics | Where is it used? | Surface color | Marking color |
| Ordinary | Does not stand out with special properties | For rooms with normal humidity conditions | Grey | Blue |
| Moisture resistant | Covered with impregnated cardboard, has antifungal and hydrophobic additives in the core material | For rooms with normal and high humidity conditions | Green | Blue |
| Fire resistant | Has special reinforcing additives in the core material | Near heating devices and open flames | Pink | Red |
| Moistureproof and fireproof | Combination of properties of GKLV and GKLO | Combination of use of GKLV and GKLO | Green | Blue |
Longitudinal edges
| Section type | Edge type | Designation | Type of installation |
| Straight | PC | Installation without joint sealing | |
| Sophisticated | UK | With joint sealing and reinforcement | |
| Semicircular on the front side | PLC | With joint sealing without reinforcement | |
| Semicircular on the front side with thinning | PLUK | With joint sealing “Uniflot” without reinforcement and “Fugenfüller with reinforcement” | |
| Rounded | ZK | Taking into account the application of plaster |
Fracture strength
| Panel thickness (mm) | Critical load not less than, H(kgf) | Deflection no more than (mm) | Deflection no more than (mm) |
| Longitudinal sample | Transverse sample | Longitudinal sample | Transverse sample |
| Less than 10 | 460 (45) | 150 (15) | — |
| 10-18 (inclusive) | 600 (60) | 180 (18) | 0,8 |
| Over 18 | 500 (50) | — | 1,0 |
GKL from Knauf with PLUK edge
Before we say what is better - GVL or GCR, or GSP, we will deal with each material separately, and let's start, as you understand, with GCR. Essentially, it is dry plaster made of gypsum (in English it sounds like “drywall”), where the filler is enclosed between two layers of thick paper or cardboard.
The material was originally intended for leveling walls and ceilings. But progress, of course, does not stand still, and therefore the sheets quickly found application for various structures such as arches, niches and shelves, figured ceilings and partitions, etc.
Such a complex structure can be built using gypsum boards
By the way, for the CIS countries such material is by no means know-how - in the Soviet Union, sheets began to be used back in the 50s of the last century, it’s just that dry plaster gained the greatest popularity only in the 21st century.
GKLV is good for finishing with ceramic tiles
Now such sheets can serve as a rough base for laying ceramic tiles, not to mention putty, painting and wallpaper, since, thanks to special additives, they have increased moisture resistance.
Plasterboard arch
Moreover, at this time the construction market offers sheets that have a certain fire resistance. We are not even talking about flammability; the material resists open fire for a certain time.
Fire-resistant plasterboard tests passed successfully!
Then manufacturers went even further - they combined fire retardants with hygroscopic additives and got GKLVO, which is very convenient in specific conditions. However, its price is certainly higher than the others.
In terms of width, all sheets have a certain standard, this is 1200 mm, but their length and thickness differ, depending on the specific need and destination. So, the length of such panels can be:
- 2000 mm,
- 2500 mm,
- 3000 mm,
- 4000 mm.
By thickness you can find the following material:
- 6.5 mm and 8 mm – ceiling;
- 9.5 mm and 12.5 mm - wall.
But the instructions do not at all limit its use for walls or ceilings, and currently sheets of different thicknesses can be used in structures.
Dimensions of plasterboard sheets
If we distinguish between plasterboard and gypsum fiber based on their decorative qualities, then gypsum board will certainly come first, although it does not have any decorative value in itself. But the whole point is that it is from such a sheet that all figured structures are made, where there is no room for the use of GLV and GSP.
This material is comfortable in every way
In addition, drywall has a significant advantage in terms of price, since other materials are much more expensive and therefore have lower popularity.
GVL
Table of nominal sheet sizes
| Parameter | Meaning | ||||
| Length | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 | 2700 | 3000 |
| Width | 500/1000/1200 | 500/1000/1200 | 500/1000/1200 | 500/1000/1200 | 500/1000/1200 |
| Thickness | 10.0; 12.5; 15.0; 18.0;m20.0 | 10.0; 12.5; 15.0; 18.0;m20.0 | 10.0; 12.5; 15.0; 18.0;m20.0 | 10.0; 12.5; 15.0; 18.0;m20.0 | 10.0; 12.5; 15.0; 18.0;m20.0 |
GVL strength table
| Nominal sheet thickness, mm | Bending strength, MPa |
| Up to 10.0 incl. | 6,0 |
| St. 10.0 to 12.5 “ | 5,5 |
| “ 12,5 “ 15,0 “ | 5,0 |
| “ 15,0 “ 18,0 “ | 4,8 |
| “ 18,0 “ 20,0 “ | 4,5 |
| “ 20,0 | 4,3 |
GVL Knauf with seam edge
Now pay attention: gypsum fiber and plasterboard - the difference lies mainly in the fact that gypsum fiber board is reinforced with various technological additives and cellulose waste paper. Therefore, it is more durable, although more expensive.
The main similarity of the material is that their main component is building gypsum, but there is no cardboard shell. You can see from the tables above that this sheet has a much higher density, which actually allows it to be used as a rough floor covering, known as a dry screed (GOST R 51829-2001).
Differences in edges: a) straight, b) folded
If we talk about the configuration, then again it is impossible to say which is better - plasterboard or gypsum fiber, although the latter has more dimensions than those proposed by the manufacturer. But it has only two types of edges - straight and folded, but in this case this is quite enough for finishing work.
There are only two types of these sheets (however, even on this basis it is difficult to judge which is better - GVL or plasterboard) - ordinary and moisture-resistant (GVLV). But they all:
- according to GOST 12.1.044 they belong to group T1 in terms of toxicity;
- according to GOST 30402 to group B1 for flammability;
- according to GOST 30244 to group G1 for flammability.
Dry screed: laying sheets
Application of gypsum fiber sheet:
- as you already understood from what was written above, gypsum fiber sheets at the household level are most often used for arranging rough floor coverings - as a dry screed;
- they are laid either on a flat surface such as concrete floors or wooden flooring, or on fine expanded clay, with a fraction of no more than 5 mm (for insulation);
- such a rough base can be used for almost any floor covering - ceramic tiles, parquet, laminate, carpet, linoleum;
- in addition, in order to increase fire safety, gypsum fiber can be used as wall cladding, which will simultaneously serve as dry plaster;
- it is possible to use these sheets in various utility and domestic premises, not only for finishing, but also as a material with increased moisture resistance;
- if necessary, the material can be used for the installation of interior partitions and suspended ceilings, but, as you understand, it will be somewhat more expensive than plasterboard.
SHG
Gypsum particle boards
Technical characteristics of GSP
| Name | GSP/GSPV (TU 5742-004-05292444-2010) | |
| Density (kg/m3) | 1200±50 | |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 8-9 | |
| Internal pressure strength (MPa) | 0,3-0,4 | |
| Modulus of elasticity (MPa) | 3000-4000 | |
| Vacation humidity (%) | 2,0±0,5 | |
| Ud. resistance when pulling out screws (N/mm) | 60-105 | |
| Volumetric water absorption (%) | 2h | 20-28/5-10 |
| 24h | 23-30/10-15 | |
| Swelling by thickness (%) | 2h | 2/0,2 |
| 24h | 3/0,5 | |
| Thickness deviation (mm) | Not polished: at 8-10 mm ±0.6 mm, at 12-16 mm ±0.8 mm; grinding: ±0.3 mm | |
| Environmental friendliness | 1 class (40-60 Bq/kg), NRB 99/2009, PG11 | |
| Fire hazard | G1, V1, D1, T1, RP1 | |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient (W/m*C) | 0,21-0,25 | |
| Airborne noise insulation index (Rw, dB) | 32-35 | |
GSPs are widely used in repair and construction work
If we talk about the composition of the material, there are three main components:
- building gypsum – 83%,
- wood shavings – 15%,
- and moisture 2%.
In the production of the board, semi-dry pressing is used: a moistened substance consisting of building gypsum and wood chips is evenly distributed on a steel sheet and pressed at normal temperatures. It is noteworthy that the outside of the panel is dense, smooth and light.
SHG composition
GSP size table
| Meaning | Parameters (mm) |
| Length | From 500 to 3000 (polished 2500, 3000) |
| Width | 1250 |
| Thickness | 8, 10, 12 (polished 8,10) |
| Along the perimeter | 3000×1250, 2500×1250, 500×1250 |
Despite the presence of wood in its composition, this material clearly meets all fire safety requirements, as you can see for yourself from the table above.
Production of gypsum particle boards
This is achieved due to the fact that the main part of the heat during a fire is spent on the dehydration of gypsum (splitting or evaporation of water), which allows it to not ignite for a long time. Also, wood does not contribute to the susceptibility of the slab to the formation of fungus or the possibility of the growth of any bacteria.
Gypsum particle board has a perfectly smooth surface, which allows it to be successfully used as a rough finishing material. The material can be the basis for ceramic tiles, laminate, parquet, linoleum, carpet.
The photo shows the process of installing GSP on the floor, in other words – dry screed
Application of GSP:
- gypsum particle boards can be used in almost all commercial, domestic and residential premises, hospitals, kindergartens, shops and offices;
- The main purpose of the material is the manufacture of partitions, leveling walls and ceilings, dry screeding and even leveling window sills.
It is noteworthy that such a slab can also be laid as a dry screed, painted, and also act as a finishing element, but, of course, under a carpet.
Classification of gypsum fiber sheets
Standard version (GVL). Designed for finishing interior spaces with normal and average humidity levels.
Moisture-resistant material (GVLV). It has a minimal moisture absorption rate and is able to retain its shape during prolonged contact with water.
GVL is produced in the form of gray sheets with blue markings indicating the modification (standard or moisture resistant) and dimensions.
Properties of GVL:
- Gypsum fiber products are characterized by high strength and resistance to moisture.
- The material can withstand a greater number of freezing and thawing cycles compared to its plasterboard counterpart (15 cycles instead of 4).
- The noise insulation properties of gypsum fiber are also higher (reduces the noise level to 35 dB, while plasterboard suppresses noise to 25 dB).
- The longitudinal edge of gypsum plasterboard can be straight or folded, which in some cases simplifies the finishing process.
We advise you to study - Types of sliding doors and their design features
Main technical characteristics of gypsum fiber
Unlike gypsum plasterboard, gypsum board has higher strength properties and can be used for finishing a wider range of objects. Under severe operating conditions, gypsum fiber demonstrates increased resistance to negative climatic influences.
Comparison of GVL with analogues
First, let's figure out what GVL is. It differs from standard drywall mainly in its manufacturing technology. If the sandwich principle is used in the production of plasterboard (that is, two layers of cardboard and a gypsum layer between them), then in the case of gypsum board, manufactured fibers are mixed into the gypsum mixture and pressed into the form of a sheet. This results in increased strength and excellent fire performance. An analogue of GVL SML is a fairly new finishing material made in China. The glass-magnesium sheet contains in its structure magnesium oxide, finely dispersed shavings, perlite, magnesium chloride and binder composite materials. One of its good qualities is its non-flammability. In this regard, none of the currently known materials can compare with LSU. GVL is also inferior to it in fire resistance.
It is impossible not to note the moisture resistance. LSU perfectly withstands high humidity conditions. Test results have proven that even after immersion in water for several hours, the LSU does not lose its shape. It is also not susceptible to mold, deformation, does not contain harmful substances, flexible, durable, lightweight and quite easy to use. But in our country this material has not yet been studied enough, so not everyone risks getting involved with it, preferring GVL or GCR. GCR is the most common option. This is a composite finishing material that is traditionally used for finishing residential and office premises. Drywall is environmentally friendly and does not contain any harmful impurities. Excellent soundproofing characteristics and non-flammability make it the most common and versatile material for constructing interior partitions, leveling walls and installing ceilings. property is interesting
when the humidity in the room is high: the material absorbs excess moisture, and when the air is dry, it releases it. GVL is, in fact, an improved version of gypsum plasterboard, superior to it in some respects. For example, increased strength and fire resistance. In general, GVL has a huge list of advantages:
- Excellent heat and sound insulation.
- Environmental friendliness and safety.
- Increased strength.
- Easy to use.
- Low amount of waste during installation.
- Possibility of mounting on both wooden and metal frames.
- Another quality that can be noted is the ease of processing of joints.
- It is not necessary to use special tools to cut gypsum fiber board.
The list of shortcomings is not so impressive. It is limited by a large mass that prevents deformation and stretching. You won't be able to bend it like drywall. And the second drawback is the high cost compared to the same drywall.
In what cases is it better to use
Having found out the advantages and disadvantages of the materials in question, you can decide which is better, plaster or drywall for walls in each specific case. To make a decision, you will need to analyze the input data: the degree of deviation of the vertical wall, the base material, whether the manufacture of complex structures is required to give the interior the intended appearance, operating conditions of the room, the need to mask any structures and communications, what material is planned to be applied as finishing cladding on the walls and the experience of the master.
Drywall
To resolve the doubt whether it is possible to cover the walls with plasterboard instead of plaster, the following list of circumstances in which the installation of plasterboard is preferable will help:
- if the base is a wooden surface, for example, in a country house or country house, when they are a permanent place of residence;
- if necessary, disguise internal communications without the use of tedious gating and if there is free space in the room;
- if there is a need for additional insulation of the room or sound insulation;
- with significant differences in the vertical wall (more than 20 mm);
- if it is necessary to complete finishing work in the shortest possible time;
- when doing the work yourself, when it is not possible to hire a professional to plaster the walls;
- if necessary, eliminate flaws in masonry made of aerated concrete, gas silicate blocks, bricks and foam blocks;
- in cases where it is necessary to eliminate protruding parts of the foundation made of FBS.
In ambiguous conditions, when it is possible to use both materials, you should calculate whether it is cheaper to level the walls - with plasterboard or plaster, and then make a decision.
Plaster
If you need to decide how best to level the walls - with plasterboard or putty, the main criterion for making a decision is the magnitude of the vertical difference of the base and the purpose of the room.
For small vertical deviations, you can use gypsum plasterboard and plaster the surface, but if you are going to hang heavy shelves or other objects on such walls, you will only have to plaster the base.
Leveling plaster is used in the following cases:
- when preparing bases for subsequent finishing with heavy materials (decorative stone slabs);
- for leveling the surface in rooms with high humidity levels (in the bathroom);
- if it is necessary to secure massive objects to the walls;
- in small rooms when you need to save space;
- when the treated surface deviates from the vertical within 20 mm;
- in rooms where sudden changes in temperature and humidity conditions are possible.
Plaster is a good option for wall finishing, especially if it is gypsum, cement or environmentally friendly clay plaster. Is drywall or plaster better in a home? This question is a common dilemma for many people renovating their home. Modern dry building mixtures do not require much experience.
In turn, drywall can be installed using metal profiles quite quickly. In addition, gypsum boards are cheaper than plaster. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, which we will look at in this article.
Is there an alternative?
As a replacement for both options, a variety of slab materials are used:
- OSB. The products are distinguished by their rigidity and reliability, suitable for covering any base.
- LSU. Magnesium glass sheets with reinforcing layers are similar in characteristics to plasterboard.
- DSP. Cement boards with the addition of wood chips have excellent parameters that can be compared with gypsum fiber board.
GKL and GVL sheets are not the only materials for arranging various types of surfaces, they are no better or worse, it’s just that each of them was developed for a specific situation.
Such diversity allows you not only to choose the most suitable products, but also to successfully combine materials.
Drywall. Features and Applications
Drywall is a three-layer composite material consisting of modified gypsum in the middle, covered on both sides in a cardboard shell, depending on the impregnation, moisture-resistant and (or) fire-resistant. Also, various fire-resistant and antihydrophobic components are added to the core itself.
This is how it exists:
- Regular - gypsum board;
- Moisture resistant - GKLV;
- Fire resistant - GKLO;
- Fire- and water-resistant - GKLVO.
Used for several purposes:
- To create a smooth, uniform surface. Most often, plasterboard is used to cover walls, ceilings, and less often the floor due to its high fragility, however, floor blocks are still produced for rooms with light loads;
- To level the plane, in this case a frame made of metal profiles or wooden sheathing is used;
- During the construction of interior partitions;
- To disguise communications;
- As a facing covering of the frame, used for intracavity insulation and sound insulation;
- For the formation of decorative and useful structures - arches, niches, shelves, cabinets, multi-level ceilings.
Advantages of gypsum plasterboard
The main advantages of plasterboard in interior decoration:
- Plasticity and the ability to create concave structures, arcs, using a bending machine, needle roller or cuts
- A light weight
- Possibility of quick installation/disassembly and ease of cutting
- Hygroscopicity
- Low cost
- A large selection of subsequent cladding - painting, tiling, wallpapering, and so on
- Possibility of purchasing laminated gypsum board sheets that do not require finishing and puttying, as well as plasterboard blocks combined with insulation
Disadvantages of drywall
Along with the positive qualities, gypsum board has the following disadvantages:
- Low resistance to direct moisture, even with moisture-resistant cardboard treatment
- Fragility and low strength of the material
- Impossibility of using nails during installation, while the composite holds perfectly on glue or screws
- Maintaining maximum air dryness in storage conditions
- Instability to mold, mildew
Overview of gypsum board and gypsum board
Gypsum fiber sheets and plasterboard "Knauf" are very popular for wall decoration. They are also used for finishing industrial buildings, residential interiors and public buildings. But since there is a high probability of stumbling upon a fake in the building materials market, it is always worth familiarizing yourself with the Knauf plasterboard certificates of conformity, which every decent seller should have.
Plasterboard and gypsum fiber sheets from this manufacturer have different structures.
The difference is determined in operational and technical characteristics:
- gypsum fiber has an even structure, which allows you to cut the material without chipping. Therefore, GVL can be used for parts of different sizes;
- the use of GVL is required where high impact resistance is required;
- plasterboard is characterized by excellent plasticity, which allows it to be made into structures of various shapes;
- GVL and gypsum plasterboard from this company also differ in the degree of frost resistance. In this case, drywall is designed for 4 cycles of thawing and freezing, and gypsum fiber for 15 cycles.
The table below shows approximate prices for different types of gypsum fiber boards and gypsum plasterboards from Knauf:
| Photo | Kinds | Description | Prices, rub. |
| GVL sheet Knauf floor element | 200x600x1200 mm. Superpol | 337 | |
| Knauf super sheet GVL | 2500x1200. With straight edge. | 487 | |
| Knauf plasterboard sheet | 300x1200x12.5 mm Used for the construction of light partitions. | 279 | |
| Knauf plasterboard moisture resistant | 2500x1200. Used for suspended ceilings and as a covering for walls. | 336 |
Knauf gypsum board Knauf gypsum board moisture resistant
Product characteristics and dimensions
Let's consider the main dimensions of the Knauf gypsum board sheet:
| Kinds | Dimensions |
| Standard, 12.5 mm thickness, 2 meters length. | 1200×2000 |
| Thickness 12.5, length 2.5 meters. | 1200×2500 |
| Thickness 12.5, length 2.7 | 1200×2700 |
| Thickness 12.5, length 3 meters | 1200×3000 |
If you are looking for a suitable material for a bathroom, toilet room or swimming pool, then you can consider the products of moisture-resistant GVL for flooring 1200x600x20mm "Knauf" Superpol. You can also use the sheets presented in the table.
| Kinds | Dimensions |
| Moisture resistant, length 2 meters, thickness 12.5 mm | 1200×2000 |
| Thickness 12.5 mm, length 2.5 meters. | 1200×2500 |
| Thickness 12.5, length – 3 meters. | 1200×3000 |
The table shows prices for gypsum fiber sheets from this manufacturer depending on size
GKL Knauf: special characteristics
It also offers acoustic gypsum boards. This material has the following properties:
- reduces the level of background noise;
- improves perception;
- reduces boominess.
Acoustic plasterboard allows you to create a comfortable indoor environment. Therefore, finishing with such material is required in cinemas, classrooms, recording studios and meeting rooms. This material is also used in apartments.
No less popular are the types of moisture-resistant gypsum board "Knauf". It is used in the kitchen, bathroom and in places where high humidity is expected.
Features of installing partitions using Knauf products. Installation of gypsum plasterboard and gypsum board sheets is carried out using these methods.
Related article:
Watch this video on YouTube
Watch this playlist on YouTube
Previous Building materials Brick-like tiles for interior decoration: price, choice of materials and installation technology Next Building materials Chipboard: what is it and how to choose what is really profitable
Scope of materials application
In terms of popularity, gypsum board noticeably wins. In the segment of finishing materials, these products are the undoubted leader. Why is there such a difference in the demand that gypsum boards and drywall have, what is the difference? The large volume of gypsum board sales is determined by the following considerations:
We advise you to study - Mineral insulation for the walls of a frame house- The ability to implement complex decorative projects that require the production of original forms and configurations of interior elements, which in some cases will be a key factor in choosing
- Reducing the project budget. For financial reasons, projects are selected where only drywall is used. But this is not always a good criterion for creating a high-quality interior.
- Less labor intensive processing. The strength of gypsum fiber board can become an insurmountable obstacle for many home craftsmen if the work is done with their own hands. Cutting dense and durable gypsum fiber sheets by hand is not easy; you need to use the appropriate tool
The key difference between gypsum plasterboard and drywall is the qualities that the surface will have after installation. When choosing a material, it is advisable to know exactly the expected operating conditions. If the room has high humidity, if significant physical stress will be placed on the structural elements of the finishing, then the gypsum fiber sheet is beyond competition.
Modern industry offers new solutions when producing favorite products. For finishing, gypsum plasterboard can be used, which has a decorative layer applied during production. Vinyl film, imitating leather, wood, fabric, is made using high-quality printing with realistic color shades and texture, reminiscent of natural materials. One operation solves several problems at once: creating a flat surface and applying the finishing touch.
What is cheaper - plasterboard or gypsum vinyl cladding is a controversial issue. The material itself is more expensive, but during installation there is no need to do other traditional operations - puttying, painting, wallpapering the surface. The total cost of finishing is comparable, but the time and labor intensity of the process is saved.
Wall finishing with plasterboard
Installation of plasterboard boards can be done in two ways:
- dry (on profiles);
- by gluing to the surface with special glue.
In practice, these two technologies are durable and are sufficient for domestic needs.
Advantages of plasterboard finishing
- you can do this work yourself, even if you don't have much experience;
- gluing the panels is not difficult, you just need to accurately determine the location of each plate and spend a little more time finishing the wall with windows and doors.
Many people say that the advantage of drywall is that it allows you to make the wall very even and smooth. There are two points to consider here:
- This can also be done using plaster, but more experience will be required.
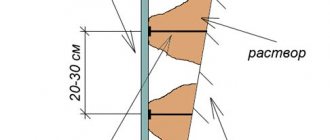
- For less experienced people, drywall will be easier to work with, but care must also be taken to ensure that the wall itself is not too crooked. The layer of gypsum adhesive must be within certain limits; it should not be too little or too much, which may sometimes require additional treatment of the walls before assembling the panels. Some problems can be solved by installing slabs on profiles, but this solution is more expensive and more labor-intensive than installation by gluing.
When installing drywall, it is important to choose the right type of slab for the room, namely, match it to the conditions where there is a certain temperature and humidity. In bathrooms, kitchens, and laundries, it is necessary to use impregnated so-called “green” boards, which have increased moisture resistance, but it should be borne in mind that they are not waterproof
After installing the panels, on profiles or with glue, a very important stage of work is the correct finishing of all joints between the panels. If we make mistakes at this stage, then over time unaesthetic cracks may appear on the surface of the walls, which spread to the paint layer.
It is also necessary to carefully control the location of places where glue is applied so that this does not lead to sagging of the slab, for example, when hanging heavy shelves on the wall, which can even lead to a crack in the slab.
Disadvantages of plasterboard finishing
- high water absorption;
- complete disrepair in case of flooding by neighbors;
- less strength and load capacity;
- the thickness of the wall will steal the area of the room.