SHARE ON SOCIAL NETWORKS
FacebookTwitterOkGoogle+PinterestVk
Hardboard: what is it? This product is classified as a sheet building material made from various types of waste from the paper, wood and woodworking industries by hot pressing with various additives. In a broader concept, these are wood fiber boards (DFB), but with certain physical and mechanical properties and qualities. The article discusses the characteristics of this material in more detail.
Hardboard is an indispensable material when carrying out finishing work.
Fiberboard and its types
Fibreboards are fibreboards made from thin wood fibres . They are mixed with binding resins and formed into a carpet, which is sent under the press. Depending on the pressure at the outlet, slabs of different densities are obtained:
- low (LDF plate);
- medium (MDF board);
- high (HDF board).
Fiberboard boards differ not only in density, but also in the type of processing. They can be sanded or unsanded, painted, film-coated, or laminated. Each type of material has its own name.
Marking and quality of hardboard
Hardboard is labeled depending on its properties and characteristics. The type of hardboard should be chosen depending on its intended purpose.
The difference in the quality and purpose of hardboard sheets is visible to the naked eye. Some sheets have a face covering, others do not. The surface of the sheet may be smooth on one side, or maybe on both. Decorative coating on the front side and a corrugated surface on the back.
The smooth decorative surface of hardboard is created by lamination, painting, film, plastic or varnish.
Hardboard sheets with a reverse corrugated surface are used for leveling walls, ceilings, floors, as well as for the manufacture of containers and packaging, i.e. where decoration is not needed. This material is very practical and cheap.
Hardboard board without coating
Therefore, for rough work you can use the cheapest brands of hardboard.
Hardboard for decorative finishing will cost a little more. Not only does it have a beautiful appearance, but its quality is also somewhat higher: such slabs are harder and, accordingly, stronger; their surface is laminated or trimmed with other decorative material.
Since the production of fiberboard has long been regulated by law, their types and markings are clearly regulated by GOST 4598-86 and include the following designations and categories:
- “M” indicates the softness of the material;
- “NT” grade PTs220 - semi-solid, low-hardness material;
- “T” brand Ts450, 400, 350, 300: solid board without decorative finishing on both sides;
- “ST” brand STs500 super-hard board, without finishing the front side with fine wood;
- “TP” front side is treated with paint;
- “TS” one side of the fiberboard includes wood;
- “TSP” - combines a painted surface;
- “TV” moisture-resistant board, without finishing;
- “TSV” waterproof material, one side of the board is made of fine wood;
- “STS” is a super-hard type of fiberboard, with one-sided coating of fine wood;
- Fiberboard with decorative surface finishing;
- Fiberboard without decorative surface finishing;
What it is?
Fiberboard (fibreboard) is made from industrial waste, softened and brought to a homogeneous state. This material has several varieties, differing in strength, hardness and type of external surface finish. All materials in this group are produced in accordance with GOST 4598-86, pressed into sheets with a thickness of 2 to 15 mm (some types reach 40 mm in this indicator). Thin varieties demonstrate good flexibility and are suitable for cladding curved structures.
The raw material for the production of fiberboard is obtained from wood processing waste. This includes wood chips, firewood, sawdust, thoroughly washed and dried, and then crushed into fibers. The degree of grinding depends on the characteristics of the future slabs. Subsequently, the wood base is mixed with other components:
- resin-based binders;
- water repellents to increase moisture resistance;
- antiseptics to prevent rotting;
- flame retardants (for fire-resistant materials).
The process of forming slabs from raw materials occurs under a pressure of 3-5 MPa with heating up to +300 degrees Celsius. Hardboard is a material that does not have a separate class, since it is included in the list of subtypes of fiberboard. The difference lies mainly in the hardness of the sheets and their characteristics, as well as in the production method.
Another type of fiberboard is informally called masonite - it is obtained using the wet method, while hardboard is dry pressed.
Dimensions of hardboard sheets
Manufacturers offer hardboard sheets of different sizes: in length they can reach from 1 m 20 cm to 6 m; in width from a meter to a meter and eighty cm. Large fiberboard slabs are relevant for industrial scales.
For domestic construction needs and small furniture production, standardized sheets with parameters of 2140x1220 or 2750x1220 mm are used.
The dimensions of fiberboard (hardboard) slabs are presented in the table:
Attention! Before purchasing whole sheets of hardboard, you need to decide on their dimensions for organizing transportation and the possibility of placing them in their entirety at the work site. Many manufacturers and distributors of hardboard slabs provide cutting services according to the parameters specified by the buyer.
Any type of fiberboard board is manufactured in accordance with GOSTs 4598-86, 19592-80 and 8904-81, with minor changes that are relevant in modern conditions.
These documents standardize not only production, but also the size of the slabs.
The table shows an excerpt from GOST 4598-86 on the permissible sizes of hardboard slabs:
In turn, hardboard sheets can be manufactured to individual order, taking into account customer requirements in terms of size and decorative finishing, but without violating standards for marking and production technology.
The thickness of standard fiberboard boards varies from 2.5 mm to 40 mm. This thickness indicates that the sheets are quite thin: whether this is a plus or a minus depends solely on the scope of application of these panels.
The thickness depends on the density of the sheet. Sheets with low and medium density are made from 8 to 16 mm thick. Sheets of this thickness are applicable as a noise and heat insulating material for partition walls, but are absolutely not suitable for finishing.
For semi-hard hardboard slabs, the thickness ranges from 6 to 12 mm, and for super-hard boards, from 2.2 to 6 mm. It is panels with this range of thicknesses and technical characteristics that are suitable for floors, walls and ceilings.
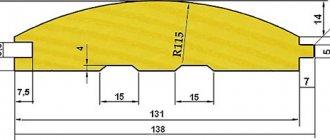
Design drawing for subfloors made of hardboard (fibreboard)
Advice! The choice of hardboard brand depends on the place where it will be used. In most cases, it is worth giving preference to moisture-resistant types of fiberboard.
Advice! When purchasing hardboard sheets, carefully check each panel for defects: chips, scratches, depressions and unevenness.
To conclude the topic about hardboard, please note that today this material is very popular due to its low cost, practicality and versatility. It is easy to work with and is suitable for the manufacture of joinery, packaging, partitions and finishing of any indoor surfaces, rough work and temporary structures. The variety of fiberboard allows you to solve many construction problems.
Hardboard - composition and properties of the material
Areas of its application, properties and purpose of the material
Hardboard is a sheet form factor material widely used in construction. The material is made from various types of waste from paper and woodworking industries by hot pressing with specialized additives. In a broad sense, hardboard material is ordinary wood fiber boards (DFB), but with technologically developed physical and mechanical properties. In the article we will go into detail and present the entire set of characteristics of the material under study.
Hardboard - what is it? Composition, properties and scope of application of the material
Overview characteristics of fiberboard
Hard and soft deciduous and coniferous trees, bast plants with a fibrous structure (reed, cotton, reed) can be used as raw materials. Phenol-formaldehyde resin, less often pine rosin (usually to strengthen soft boards) or organic isocyanates are used as a binder. Also, in order to adjust certain properties, add:
- repellents in solution with an aqueous alkaline emulsion (paraffin, ceresin, distillate slack);
- impregnation (on tall oil with the addition of driers, gossypol resin, recycled polyethylene or petroleum bitumen);
- precipitants (sulfuric acid, aluminum sulfate);
- flame retardants (nepheline with asbestos or phosphates, ammonium sulfates, boric acid or borax);
- antiseptics (ammonium silicofluoride, sodium pentachlorophenolate).
The table provides a description of the production technologies for standard fiberboard sheets.
| Stages | "Wet" method | "Dry" method |
| Preparation of raw materials | Chopped wood chips are sorted according to a number of parameters: no crushed lumps, length 10-35 mm, thickness up to 5 mm, cut 30-60 degrees. Acceptable content is 1% minerals, 5% rot, 15% bark. | |
| Humidity and strength of raw materials | Before grinding, the moisture content of the material is 50-70%, after - about 30%. To reduce the fragility of the fibers, the wood chips are steamed at +80-90 degrees Celsius. | |
| Forming the slab | The fibers are placed in a pool where the water content in the working mass reaches 98.2%. Next, the composition is filtered and squeezed. The residue on a mesh base is pressed at a temperature of 200-215 degrees Celsius, a pressure of 5-5.8 MPa. The raw materials go through three stages here: pressing, drying, hardening. | The canvas is formed in the air. The raw materials in the steaming chamber are irrigated with a binder solution. The carpet is pressed at a temperature of +220-260 degrees Celsius under a pressure of 6.5-7.5 MPa. Drying is carried out in 2 stages, finally conditioning with humidification and cooling. |
| Additional processing | After oil impregnation, solid slabs are subjected to heat treatment (+160-170 degrees Celsius). Soft sheets do not go through this stage. | Before the conditioning stage, heat treatment is carried out to increase the resistance of the boards to water and mechanical stress. |
Compared to the natural analogue, the fibrous analogue costs less, exhibits better flexibility or elasticity, and is easier to install without the risk of cracks. Also, the sheets weigh little and can be made of fiberboard in different sizes in the form of a seamless fabric. There is still one drawback - the narrow scope of application of a particular subspecies. For example, for walls or floors, rough cladding or decorative.
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in finishing materials and related work
Classification and labeling
Unlike hardboard, fiberboard sheets, which are made using the “dry” method, have 2 smooth sides. Accordingly, materials are awarded categories “A” or “B”. The latter are considered more durable and resistant to moisture due to a larger number of different functional additives.
Finished fiberboard sheets have different standard sizes, appearance, technical characteristics and scope of application. Markings and main classification are given in the table.
| Subspecies | Decoding | Distinctive features |
| M | Soft | Porous, low strength. Based on density, three subtypes are distinguished and designated by a numerical identifier: 1, 2, 3. |
| NT or PT | Reduced hardness | Absorbs up to 40% moisture, exhibits good resistance to mechanical load, hard. |
| T | Solid | Swells from moisture by 20-25%. Durable boards with mechanical resistance. Additionally, materials are divided into groups “A” and “B”. |
| TS | Solid with a smooth or decorative side | |
| TP | Solid hardboard with painted side | |
| TSP | TS plus painted surface on the front side | |
| TV | Hard and moisture resistant sheet | |
| TSV | Solid, moisture resistant with fine wood finish | |
| ST | Super hard sheet | Moisture resistance of about 13% and 10%, respectively, increased density, high quality. |
| STS | Super hard board with decorative finish |
Additionally, varieties are determined. The 1st is characterized by the absence of visible flaws. Second, dents and scratches on the front side are acceptable, but do not affect the quality of the canvas.
The thermal conductivity of the canvas varies between 0.046-0.093 W/m*K. The density of soft fiberboard does not exceed 350 kg/cub.m. A cubic meter of NT or PT type sheets weighs from 850 kg, super-hard boards from 950 kg.
Fibreboard flooring finishing
Fiberboard may not always serve as a floor finishing option. Or rather, it can be left as the final version, but such a coating looks ugly. Typically, fiberboard sheets are covered with some type of finishing material.
Types of flooring
Before work (especially if painting is planned), the material is carefully prepared:
- Remains of glue are removed, nail heads are masked;
- the remaining gaps between the sheets are puttied;
- all garbage is swept away;
- all stains are treated with a degreaser;
- only after this the front side of the fiberboard can be painted or varnished. Without this preparation, the floor may turn out unsightly and with defects.
Finishing will help extend the service life of the material. Paint or varnish is applied in two layers.
Painting fiberboard floors
Areas of use
Most often, hardboard is used as a finishing material.
With its help, the walls, ceiling and floor are leveled.
To create a perfectly flat surface, no careful processing is required.
Hardboard sheets hide all defects and irregularities.
Any finishing coating can be installed on top of them without additional plaster.
Hardboard with a refined front side can itself become a finishing coating. In particular, laminated sheets can be used as flooring in rooms where abrasion loads are low.
In frame houses, hardboard is often used to make partitions. In terms of its strength characteristics, it significantly exceeds traditional drywall. Small thickness cannot ensure the rigidity of such structures, but in utility rooms this is not so important.
READ MORE: How to install heating meters in an apartment: paperwork and installation
Decorated hardboard is widely used in arranging the interiors of buses, trolleybuses, cars and even airplanes. This covering of walls and partitions does not require additional coating. The material is also suitable for control panels and instruments.
In furniture production, hardboard is widely used in the manufacture of back walls and bottoms of sofas, armchairs, and drawers. When assembling homemade furniture, this material is often used for cladding cabinet objects.
In the manufacture of containers for various purposes, hardboard has seriously replaced boards and plywood. It is used to make boxes for fragile goods, as well as packaging for transporting not too heavy loads.
Laminated hardboard
This type of sheet needs to be mentioned separately, because it is a decorative material with which you can not only create some kind of building structures, but also give them a certain appearance in terms of decorative design. Most often, this name refers to slabs lined with a polymer film. It is this that gives the material improved performance characteristics. Which ones exactly:
- increased mechanical strength, because the laminate protects the base material from scratches, cracks and chips;
- variety of design, in this regard, film offers enormous opportunities for creating drawings, patterns and other decorative imitations of natural materials: brick, stone, sand, wood, leather, metal, etc.;
- long-term operation, as stated by the majority of manufacturers. Their laminated hardboard will faithfully serve for a guaranteed 20 years;
- practicality of the material, the laminated surface gets dirty less easily, but is easy to clean with ordinary household detergents.
Laminated models
It should be noted that laminated hardboard is much more expensive than conventional models.
But even within its group there are cost differences, which depend on the laminate coating used, as well as on the brand.
Fiberboard ceiling finishing
Such slabs are distinguished by the size and number of joints located on four sides. In a short time you can get a cozy and beautiful room by finishing the ceiling with hardboard. Fiberboard can also serve as additional thermal insulation, which is very important for houses with a cold attic.
The shrinkage of a house often leads to cracks appearing on the surface. It is not uncommon for plastered walls and ceilings to become covered with small cracks several months after repairs. This does not happen when using fiberboard to decorate a room.
The All-fanera company sells panel materials such as fiberboard, chipboard and MDF, various types of plywood, and also carries out sawing and cutting of materials to order. You can buy fiberboard and other materials at both wholesale and retail prices. The goods are also delivered and packaged to prevent damage.
Many people often confuse fiberboard and hardboard. In fact, these are the same material, except that hardboard is more durable. Hardboard sheets are familiar to most consumers: these are slabs up to 7 mm thick, with a characteristic rough “checkered” back side and smooth on the front side.
Comparison of characteristics
The main difference between hardboard and other types of fiberboard lies in the characteristics of the finished material. Among the important differences are the following.
- Thickness _ Hardboard sheets are produced with a thickness of up to 15 mm, less often - up to 40 mm. Soft fiberboards are most in demand in thin sheets of 2-8 mm.
- Durability . Standard values for fiberboards vary in the range of 100-500 kg/m3. For hardboard this parameter is 550-1100 kg/m3. Twice the strength makes the material in sheets similar in characteristics to solid wood.
- Thermal insulation properties. Wet pressing makes the material porous. There is even a special type of fiberboard with the prefix “M”, suitable for increasing the soundproofing and thermal insulation characteristics of rooms. High-density slabs do not have such capabilities.
Having found out what the difference is between hardboard and masonite (fibreboard), produced by wet pressing, you can correctly determine the scope of application of the material. Solid slabs are not very flexible, but have higher load-bearing capacities. Moisture-resistant options are suitable for finishing the external walls of buildings; conventional ones are used for laying floors, creating internal partitions, and in the production of furniture and packaging containers.
A thin sheet of fiberboard bends well, so it can be used to create arches and other curved structures. In addition, the material is environmentally friendly and safe for health.
To learn how to lay fiberboard on a wooden floor, see the following video.
Hardboard: what is it? General concepts and methods of manufacturing material
The method of manufacturing fiberboard is regulated by GOST 4598-86. This technical concept refers to a material that contains various materials, including relatively soft ones. Hardboard is a common name and is not mentioned in the specified regulatory document. The front surface of the slabs is usually smooth, and can be varnished, painted, lined with plastic or decorative film. The main difference between this material and fiberboard is its structure, namely hardness. Hardboard is usually called only dense sheets, one side of which is a decorative front. Photos of hardboard clearly demonstrate its structure.
Hardboard is used for interior decoration
This material greatly simplifies and speeds up finishing and construction work, and is indispensable for cladding walls and ceilings, laying floors, and constructing internal partitions. In practice, there is no alternative to hardboard in the manufacture of furniture, containers and packaging. Its main advantages are its low cost, ease of cutting, processing and installation.
How to cut hardboard
If you need to make small cuts and process several sheets, then a regular hacksaw blade for metal can handle it. To do this, it is placed in a special holder or one side is wrapped with electrical tape.
Hacksaw blade for cutting, on a special holder
Note! Using a wood saw is strongly discouraged as it will fray the edges of the sheet being cut.
If it is necessary to process large volumes, use a jigsaw or a hand-held circular saw. In this case, for both tools it is advisable to choose a cutting element with an edge designed for metal.
Regardless of the tool used, the cutting process places the sheet on a wooden backing with the right side facing up. In some cases (to fit elements), trimming with metal scissors or garden sectors is allowed. However, this processing method can leave kinks and cracks on the edge.
Hardboard with an untreated and unlaminated front side is recommended to be painted to protect it from moisture
You can also cut out small elements of the sheet using a regular stationery knife. More details about this in the video:
Advantages and disadvantages of fiberboard
Finishing premises using fiberboard has a number of advantages, such as:
- Soundproofing. Thanks to this, the material can be used for finishing rooms in multi-storey buildings with low sound insulation or finishing houses located in noisy areas. It is also appropriate to use fiberboard in radio and recording studios.
- Thermal insulation. The fibrous structure of fiberboard closes all the cracks and cracks in the walls, which allows the material to be used for insulating floors, roofs and walls. This is especially true when it comes to a wooden house.
- Long service life. By compressing the fibers, the material becomes dense and can last for decades.
- Environmentally friendly. The porous structure of fiberboard conducts air well and protects the room from heat and stuffiness.
- Convenience. The natural structure of the material allows you to regulate the temperature and humidity in the room naturally. When using fiberboard to decorate a country house, much less time is spent on heating it. At the same time, there is no “echo” effect characteristic of drywall.
The disadvantages of fiberboard include the limited scope of application. In addition, the material may not withstand the direct impact of water flow if the apartment is flooded by neighbors. Due to the thinness and flexibility of the material, it is more convenient to install fiberboard with an assistant who will hold the slab.
Hardboard design
The raw building material has a cork structure. The presence of a coating of finely divided wood pulp gives smoothness. The shade is close to natural: from light beige to brown. Products can be painted white, black and other colors.
Laminated sheets come in different designs. For example, hardboard panels for walls are made to imitate the structure of wood, stone, tile, and brick. They can be used for decoration.
Variety of slab designs.
Hardboard: what is it? Material composition
To impart certain properties to the material, appropriate components are included in the raw materials during the production process. Adding the necessary substances allows you to improve one or another indicator. The composition of fiberboards includes the following components:
- binders (synthetic and phenol-formaldehyde resins) make it possible to obtain a dense and durable structure;
- polymers (pectol, etc.) improve strength and mechanical properties;
Untreated hardboard can be used for finishing
- hydrophobic substances (paraffins, rosin, etc.) are used to give the product moisture-proof and moisture-repellent properties;
- antiseptic components improve biostability and prevent mold and rotting;
- Fire retardants provide a certain resistance to fire.
Technical documentation allows only low-toxicity resins for use. The binder content in the material should not be more than 1.3% of the total initial mass.
Hardboard is a fairly durable material
Labeling and quality
Hardboard grades are divided into types according to physical and mechanical characteristics. These qualities must be taken into account when choosing it.
The difference can be seen immediately upon external examination. The surface of the slabs may or may not have a coating, and be smooth on one or both sides. There are products with a decorative layer on only one of the surfaces, while the reverse has a corrugated structure. The smoothness of the material can be achieved in various ways: painting, varnishing, applying film or plastic, lamination.
The corrugated surface of the back side of the sheet makes the material cheaper. It is ideal for gluing to durable surfaces and in cases where decorative function is not important.
The surface of hardboard slabs may not have a coating
There is no need to purchase denser and, accordingly, more expensive fiberboard sheets if they are intended only for rough work. On the contrary, if the material will be used for external decorative finishing, then it is better to use harder and more durable boards covered with laminated film. Accordingly, such hardboard sheets will cost more, but in this case it is justified.
Conventionally, the entire variety of hardboard can be divided into the following types:
- soft material "M";
- semi-solid material “NT” (grade PTs220);
- hard material “T” (grade Ts450, 400, 350, 300);
- superhard material “ST” (grade STs500);
- sheets with refined surface;
- sheets with untreated surface.
Characteristics of hardboard by surface density
The marking “M” means soft hardboard. The sheet has a density from 100 to 500 kg/m?. Visually, the surface structure resembles cork. It can be used for interior finishing work (walls, ceilings, floors) and partitions.
There are many types of hardboard
The “T” marking refers to hardboard. Does it have a density in the range of 500-800 kg/m? and visually its structure is similar to cardboard. The material has a certain moisture resistance, especially in combination with moisture-resistant coatings, and has strength when bending the sheet. Hardboard can be used in construction work, used in the production of containers, furniture and carpentry.
The marking “ST” means super-hard hardboard. It has a density of 800-1100 kg/m?, has a very durable structure and can be used in construction, furniture production and other fields.
Hardboard is often stylized as wood
Since this material can be considered a type of fiberboard, their labeling and classification are the same. According to GOST 4598-86, products differ in surface type, density and strength:
- “T” – hard sheet with untreated front surface;
- “TS” – a hard sheet with a front layer of fine wood pulp;
- “T-P” – hard sheet with a painted front surface;
- “T-SP” – a solid sheet of finely divided wood raw materials with a painted front surface;
- “T-V” – a hard sheet of increased water resistance with an uncoated surface;
- “T-SV” is a hard sheet made of finely divided wood raw materials with a painted front layer and increased resistance to moisture;
- “NT” – low-density hard sheet (or semi-hard);
- “ST” – super-hard sheet of increased density and strength with an untreated front surface;
Hardboard can be painted
- “STs” is a super-hard sheet made from finely divided wood raw materials of increased strength and density with an ennobled front layer.
Solid wood fiber sheets of grades T, TP, TSP and TS, depending on their physical and mechanical characteristics, belong to groups A and B, and are divided according to surface quality into grades I and II.
To improve the surface of hardboard, paints, varnishes or films are used. A universal option is white hardboard. Most often it is used in the manufacture of interior surfaces of furniture, cabinets, drawers, as well as in the production of containers.
General characteristics of fiberboard brands are given in the table:
| Material characteristics | M3 | M2 | M1 | NT | ST | T, T-S, T-P, T-SP | T-SV, TV |
| Humidity, % | — | — | — | — | — | 5 | 3 |
| Density of fiberboard, kg/m? | 100-200 | 200-350 | 200-400 | Over 600 | 950-1000 | 800-1000 | 850-1000 |
| Ultimate tensile strength, MPa | Undefined | 0,32 | 0,3 | 0,3 | |||
| Ultimate bending strength, MPa | 0,4 | 1,1 | 1,8 | 15 | 47 | 38-33 | 40 |
| Daily swelling in thickness, % | Undefined | 40 | 13 | 23-20 | 10 |
Resistance to moisture varies among different brands of fiberboard. As can be seen from the table, semi-solid fiberboard (HT grade) swells by 40% when left in water for 24 hours. Material grade ST (superhard) - withstands the same test with a swelling of 13%. The best indicators are for the TV and T-SV brands.
Considering this property, they can be considered a moisture-resistant hardboard in their group. The TV brand is produced, as a rule, without an external coating and is used for the construction of partitions in conditions of possible humidity and for the manufacture of furniture. The T-SV brand has the same scope, but is more aesthetically attractive due to its decorative front surface.
Moisture-resistant hardboard is suitable for making furniture
Laminated hardboard
The hardboard surface can not only be given any color or a variety of designs can be applied to it. Decorating this material with plastic film is also widely used. The price of laminated hardboard per sheet is much higher, but this material has a number of advantages:
- increased mechanical strength (the decorative layer protects against accidental scratches and damage);
- practicality (laminated coating is less dirty and easy to clean);
- durability (major manufacturers claim a service life of up to 20 years);
- aesthetic characteristics (a wide selection of different shades and structures, lamination can imitate wood, stone, tile).
Laminated hardboard has high mechanical strength
Depending on the quality of the coating and the manufacturer, prices for laminated products may vary. The average cost is 950 rubles per sheet.
Features of storage and operation
The material is transported by various modes of transport, with attention paid to installing a rain awning and securing the slabs with slings and ropes . Shift of the material will lead to the appearance of defects and scratches on the surface due to friction. When loading, remove debris and dust from the plane of the sheets.
The slabs are stored horizontally with the installation of wooden linings , which are placed across the products. The length of the bars is equal to the width of the slabs, and they are placed in increments of 50 - 70 cm, so that the upper intermediate slats are above the lower ones. In large warehouses, special racks are installed. Transfer the sheets by turning them “on edge”.
Caring for the material depends on the variety. Uncoated sheets are treated with paints and varnishes to make it possible to do wet cleaning. Plates with a film or plastic layer can be washed with a damp cloth so that no moisture gets into the seams.
Cost of hardboard
Finishing the floor with fiberboard
This type of finishing saves both time and money. In order to complete the procedure, you do not need to hire workers, and you also do not need to fill the floor with a leveling mixture and lay the floor covering after drying. Finishing the fiberboard floor allows you to get a warm and smooth floor in just a few hours. The hardboard is laid on the concrete screed after treatment with a primer and installation adhesive. Laminate, linoleum or other floor covering is laid on top of the slabs. You can also simply coat the surface with varnish for additional protection.
Storage Features
Hardboard sheets are intended for indoor use, so it cannot be stored outdoors. With prolonged exposure to moisture and ultraviolet radiation, it can be destroyed.
In warehouses, products are stacked according to size and grade. The height of the stacks should not exceed 3.5 m. This will avoid excessive pressure on the material and changes in its strength properties.
During handling and storage, manufacturers must ensure that there is no mechanical impact to avoid damage to the surface of the sheets.
Storing slabs in warehouses.
Features of the production process
The hardboard production technology is based on hot pressing of a “carpet” made from a mixture of crushed wood fibers, synthetic resin filler and various additives.
Thorough grinding is ensured in special crushers (defibrators) in several stages. Industrial production of slabs is achieved by two main methods.
Wet method
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytabouten-GB
This technology option is used to produce goods of reduced quality and at the lowest cost. The crushed wood is placed in water, where it swells to form a pulp. It is mixed with a synthetic resin, whose task is to hold the fibers together.
Next, the water is removed as much as possible, and the mixture is heated to distribute the resin evenly. A carpet is laid out from it in a press in layers, which is compressed under high pressure in a heated state. After drying, the sheets are ready for use.
Dry method
Allows you to obtain hardboard of maximum density and hardness. Shredded wood is mixed with filler without the use of water, which then polymerizes, forming a monolithic structure.
Pressing, as in the first case, is carried out by heating.
Construction material: fiberboard
New technologies and building materials make it possible to produce end products of good quality and with significant savings in raw materials . One of the most popular sheet materials is fiberboard. Suitable for finishing walls and floors, installing interior partitions, and making furniture. If we compare it with similar materials, its cost will be slightly higher. This is explained by the fact that the board is of good quality and perfectly replaces natural material.
When purchasing a sheet, an assessment is made of the size, density, production time, storage and transportation conditions. But one of the main selection criteria is price. The cost of such a sheet is much more favorable than that of natural wood. In addition, it is easy to install and process.
Safety
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyen-GB
In connection with the composition just indicated, many have a legitimate question: is hardboard harmful to health?
In general, no, but there are a couple of “buts”. Some panel manufacturers use phenol-formaldehyde, which is dangerous to humans. Russian GOST 4598-86 prohibits the use of such substances. Moreover, this is an outdated production technology, used only by underground factories.
The second subtle point is combustion. When exposed to heat, some substances in the composition of hardboard can form dangerous compounds. However, if your interior partition is on fire, you will have more serious problems.
Under normal conditions, high-quality slabs are completely harmless.
Fibreboard production
The increasing cost of resources and concern for the ecological state of the environment forces many manufacturers to invent new building materials and introduce technologies that can significantly save raw materials without much damage to the quality of the final product. A clear indicator of such changes is the sphere of furniture production, where natural solid wood has been replaced by various synthetic materials.
Fiberboard sheets are widely used in furniture production
The first imported furniture, which was imported into our country in the second half of the twentieth century, with its aesthetic and durable design, showed that waste from wood processing can be used for manufacturing. Further development of fiberboard production technology has made it possible to bring the appearance of the material closer to natural wood, enriching the slabs with a special film similar in texture to wood. The production of laminated fiberboard has increased exponentially. Today this material can be purchased at a very affordable price. The sizes of the laminated fiberboard sheet are different and will satisfy any, even the most non-standard, consumer request.
Types and markings
Sheets can be smooth, with one-sided or two-sided application of a protective layer: paint, varnish, plastic, film, lamination. Such products are used for external, high-quality decoration. They are distinguished by their durability and corresponding cost.
For interior and rough work, more budget-friendly varieties of hardboard without cladding or with a corrugated back surface are suitable.
In accordance with the physical and mechanical characteristics, hardboard grades are divided:
- M - soft.
- NT - semi-solid.
- T - hard.
- ST - super hard.
- panels with an unimproved appearance.
- slabs with a refined surface.