The increase in utility tariffs in recent years has been quite large. This is especially reflected in heating prices. People living in private homes were simply forced to look for options that could help reduce costs.
The most optimal solution from a cost point of view is to insulate the walls from the outside, which reduces costs and makes the house more comfortable to live in during cold seasons.
This article will look at the best external wall insulation.
External wall insulation
Rating of the best external insulation materials
| Photo | Name | Rating | Price | |||
| TOP 3 models of expanded polystyrene foam | ||||||
| #1 | KNAUF Therm HOUSE | ⭐ 4.9 / 5 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | Knauf Therm Wall Pro | ⭐ 4.85 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | Knauf Therm Facade PRO | ⭐ 4.75 / 5 3 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| TOP 4 models of extruded polystyrene foam | ||||||
| #1 | Carbon Eco TB | ⭐ 4.95 / 5 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | Ursa XPS-N-III-L G4 | ⭐ 4.85 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | TechnoNIKOL Technoplex | ⭐ 4.8 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #4 | Penoplex Wall | ⭐ 4.7 / 5 4 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| TOP 5 stone wool models | ||||||
| #1 | Paroc Extra | ⭐ 4.9 / 5 1 - voice | Find out the price | |||
| #2 | TechnoNIKOL Technovent Optima | ⭐ 4.85 / 5 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #3 | TechnoNIKOL TechnoFas Cottage | ⭐ 4.75 / 5 2 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #4 | Rockwool Facade Butts | ⭐ 4.7 / 5 4 - votes | Find out the price | |||
| #5 | Rockwool Light Butts Scandic | ⭐ 4.7 / 5 | Find out the price | |||
What external wall insulation would you choose or recommend?
Take the survey
TOP 5 stone wool models
Rockwool Light Butts Scandic
Rockwool Light Butts Scandic
Main parameters:
- vapor permeability value of the material – 0.3 mg/m*h*Pa
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.036 W/(m*S)
- water absorption – 1 kg/m2
- density – 37 kg/m3
- flammability group - NG
This model of stone wool is produced in the form of slabs, combining not only high quality, but also the lightness of the insulation itself in terms of weight.
The slabs are made using a special Flexi technology, in which one side at the end can be springy, which facilitates the installation process
It is also important to note that the slabs are subject to 70% compression. The material is quite durable, does not leave seams or cracks and retains its properties for a long time.
Light Butts Scandic slabs are installed as a thermal insulation layer inside structures with light coatings, such as low walls or attics. Vertical and slanted walls are also suitable.
pros
- high quality;
- ease of installation;
- good thermal insulation properties and technical characteristics.
Minuses
not detected.
Rockwool Light Butts Scandic
Rockwool Facade Butts
Rockwool Facade Butts
Main parameters:
- vapor permeability value of the material – 0.3 mg/m*h*Pa
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.037 W/(m*S)
- water absorption – 1 kg/m2
- density – 130 kg/m3
- flammability group - NG
This model is used for insulating plaster facades using a thin layer. Their rigidity and density, as well as resistance to deformation, is explained by production technologies from various basalt rocks.
To install this model of heat-insulating boards, you need to use a special adhesive composition and, if desired, dowels (if you need more reliable fixation).
pros
- high quality;
- excellent thermal insulation properties;
- ease of installation;
- good technical characteristics.
Minuses
not detected.
Rockwool Facade Butts
TechnoNIKOL TechnoFas Cottage
TechnoNIKOL TechnoFas Cottage
Main parameters:
- vapor permeability value of the material – 0.3 mg/m*h*Pa
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.038 W/(m*C)
- density – 115 kg/m3
- flammability group - NG
This insulation from TechnoNIKOL is available in the form of slabs. Hydrophobic, not afraid of fire - what is needed for high-quality insulation. Made from basalt and low-phenolic binder.
This model from Technonikol is used for thermal insulation of facade composite systems and building facades.
pros
- high quality;
- excellent thermal insulation properties;
- ease of installation;
- good technical characteristics.
Minuses
not detected.
TechnoNIKOL TechnoFas Cottage
TechnoNIKOL Technovent Optima
TechnoNIKOL Technovent Optima
Main parameters:
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.036 W/(m*S)
- vapor permeability value of the material – 0.3 mg/m*h*Pa
- flammability group - NG
- density – 81-99 kg/m3
This thermal insulation material will provide not only heat retention, but also protection from outside sounds. It is not afraid of water and fire, like any high-quality thermal insulation.
This model has good vapor permeability. If so, then instead of retaining moisture it will remove it from the room and thereby improve the microclimate in the house.
Technovent Optima is used for thermal insulation of residential buildings and/or industrial plants, as well as facade systems.
pros
- high quality;
- excellent heat and sound insulation properties;
- does not retain moisture;
- ease of installation;
- good technical characteristics.
Minuses
not detected.
TechnoNIKOL Technovent Optima
Paroc Extra
Paroc Extra
Main parameters:
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.036 W/(m*S)
- flammability group - NG
- water absorption – 1 kg/m2
- density – 30-34 kg/m3
This material is great for home insulation. This model has all types of protection - thermal, heat and sound. They are produced in the form of slabs, and they themselves are not only hard, but also soft, flexible and at the same time elastic.
The model is easy to install and does not shrink after a long time. Works great even in the coldest winter. The components evaporate at a temperature of 200 degrees and melt at 1000 degrees Celsius.
Basalt wool can be used in the following places: external walls, floors, attics, etc. and so on.
pros
- high quality;
- excellent thermal insulation properties;
- ease of installation;
- good technical characteristics.
Minuses
not detected.
Paroc Extra
TOP 3 models of expanded polystyrene foam
Knauf Therm Facade PRO
Knauf Therm Facade PRO
Main properties:
- coefficient (k-t) of vapor permeability of the material – 0.026 mg/m*h*Pa;
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.038 W/(m*K);
- degree of flammability – G3;
- density – 17 kg/sq.m.
The top three should start with the Façade model from the German company Knauf. It is implemented in the form of rectangular slabs. Thanks to a special production technology, the manufacturer will eliminate shrinkage of the slabs not only during, but also after installation.
This material is proposed to be used for insulating the walls of a private house, summer cottage, as well as various non-residential premises.
Excellent moisture resistance indicators will allow this material to be used in any, even the most humid, climatic conditions. Environmental friendliness and compactness are two more criteria why this model is worth paying attention to.
pros
- good quality of the final product
- environmentally friendly material that is not harmful to health;
- excellent heat-shielding properties;
- light weight;
- moisture resistant.
Minuses
- not detected.
Knauf Therm Facade PRO
Knauf Therm Wall Pro
Knauf Therm Wall Pro
Features:
- vapor permeability value of the material – 0.026 mg/m*h*Pa;
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.042 W/(m*K)
- flammability group – G3;
- density – 12 kg/sq.m.
Next is another model of the Therm series. Energy-efficient boards are made on the basis of polystyrene foam, taking into account all the strict requirements established by the German company. This material has not only high strength, but also obvious hydrophobic properties. They will provide good insulation for private houses, summer cottages and office premises.
This insulation model is usually used for thermal insulation of a three-layer brick wall. The slabs from this company are laid after laying two layers of brick, and only after that the third layer of brick can be installed as a finishing touch.
Important! In addition to a brick wall, this model can be placed on reinforced concrete panels.
Environmental friendliness and safety are the main principles used by the manufacturer when creating these slabs. They contain no toxic or flammable reagents - only natural ingredients.
pros
- does not sag;
- environmentally friendly material;
- does not change shape even after time;
- has high heat-protective properties;
- moisture resistant.
Minuses
- not detected.
Knauf Therm Wall Pro
KNAUF Therm HOUSE
KNAUF Therm HOUSE
Characteristics:
- vapor permeability value of the material – 0.032 mg/m*h*Pa;
- thermal conductivity of the material – 0.042 W/(m*K)
- flammability group – G3;
- density – 10 kg/sq.m.
This universal insulation from Knauf is perfect for a private home or summer cottage. It is made from environmentally friendly polystyrene foam, which does not contain flammable or simply harmful elements. They insulate roofs, external walls, attics, interfloor ceilings and even floors.
pros
- versatility;
- environmentally friendly material;
- high heat-shielding properties;
- moisture-resistant material;
- withstands loads of up to 7 tons per 1 m².
Minuses
- not detected.
KNAUF Therm HOUSE
Properties of thermal insulators
Thermal insulation with mineral glass wool
Insulation for a home, regardless of the type of building, is characterized by a low thermal conductivity. But heat insulators are compared not only by this parameter. It is equally important to evaluate other characteristics that affect the durability, safety and functional properties of the material for external insulation:
- indicators of vapor permeability and water absorption;
- impact on the microclimate of the room;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- fire resistance;
- environmental friendliness and health safety;
- resistance to biological damage (mold, rodents, insects);
- physical and mechanical parameters (including tendency to shrinkage, resistance to mechanical stress, elasticity, etc.);
- noise-absorbing properties;
- installation technology and ease of work;
- the ability to create a seamless thermal insulation coating;
- possibility of application on surfaces of complex configuration with a large number of hard-to-reach places;
- strength and long service life.
When designing wall insulation, it is necessary to calculate the thickness of the thermal insulation layer using the thermal conductivity value of the selected material. Pay attention to the indicators of water absorption and vapor permeability of the insulation, because they affect the technology of installation work.
Why is external insulation better than internal insulation?
Insulation of the house has always been considered an important aspect: without this, the house will not be warm in the winter, nor will it be possible to enjoy the cold in the summer. Houses are usually insulated from the outside. The standards are specified in SP 23-101-2004.
Internal insulation options have one very unpleasant point - they take up free space in the room. Of course, the document does not prohibit insulating a house from the inside, but this should be done only in extreme cases, when it is simply impossible to insulate the outside.
Insulation from the inside, in addition to reducing free space, carries another disadvantage - rapid failure due to exposure to moisture, so most often when insulating the inside of a room, another layer is installed - a vapor barrier.
The result of the comparison is as follows: it is better to insulate a house from the outside than from the inside.
Features of installation of external panels with insulation
Installation in progress
The ease of installation of the panels is due to the smooth surface of the walls outside the house. If they are deformed or uneven, then plastering and rubbing must first be done. After all, if the surface is flat, then the slabs can be applied without lathing or frames - with glue and resins.
Step-by-step installation instructions
Don't rush during installation
Step 1. Prepare the tools: hacksaw or grinder, hammer, level, tape measure, screwdriver, marker.
Required Tools
Step 2. Align the walls - according to the level of the most convex place.
Leveling the walls
Pros and cons of external insulation
Insulating the exterior is a useful method of retaining heat and reducing costs in the long run.
This option has both advantages and disadvantages, which should be equally taken into account. Let's look at them below.
| pros | Minuses |
| The room remains warm longer, which is important in the winter season | It takes longer to warm up the house due to the thermal insulation properties of the material |
| The temperature inside the house does not change, and if it changes, it is insignificant | |
| The insulation closes the seams in panel houses, which solves the problem of their sealing | It is very difficult to insulate a multi-storey building on your own - you need to seek the help of specialists |
| Insulation will greatly increase the service life, since the outer material will act as a protective layer |
External insulation has its pros and cons, which should be taken into account when choosing
Principles of insulating the external walls of a house
It is important to understand why façade insulation is a priority over thermal insulation of residential premises from the inside. There are situations when it is not possible to install heat-insulating material and external finishing of the building from the outside; in these cases, internal insulation is the only possible option.
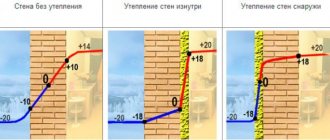
The problem is the location of the “dew point” - the place where heat meets cold, causing condensation to form. And in a living room, moisture is always present in the air due to evaporation from bodies, breathing, and the use of water for domestic needs.
The dew point in an uninsulated wall is located approximately in the middle of the enclosing structure. This means that the wall is picking up moisture from the room. If you install thermal insulation on the inner surface of the walls, the structure will freeze through and the slightest access of warm, moist air behind the insulating layer will lead to condensation - the wall will get wet under the insulation.
Experts say that it is better to insulate the house from the outside. In this case, the wall structures will be insulated from contact with cold air, as a result of which the walls will not freeze. Depending on the insulation technology used on the outside, the moist warm air that passes through the wall:
- will not come into contact with the cold, since the insulating layer is mounted directly on the wall structure;
- gets into the ventilation gap between the wall and the heat insulator, the moisture will quickly evaporate, due to which there will be no conditions for the wall to get wet - with external insulation, the dew point is located outside the structure.
To choose the best option for external insulation, you need to take into account the characteristics of the materials from which the house is built, as well as the technical characteristics of the heat insulators.
Commonly used insulation materials for outdoor use
Construction stores today offer a wide range of thermal insulation products. The three most popular materials are:
- expanded polystyrene foam (international designation - EPS);
- extruded polystyrene foam (international designation - XPS);
- stone wool.
Expanded polystyrene foam
It is considered a fairly popular option. Presented in the form of solid slabs. Their density can be different, which directly affects thermal conductivity.
The structure of this material is small balls with air inside, which are tightly fastened together, which provides excellent thermal insulation in the house.
Foamed polystyrene foam has good moisture resistance and strength. Also considered low flammable.
And yet this material has disadvantages. There are only two of them:
- when burning, it can release large amounts of toxic gas;
- they cannot insulate walls made of “breathable” material.
Example of expanded polystyrene foam
Extruded polystyrene foam
This material has some similarities with expanded polystyrene foam in terms of composition. The difference is in the production technology, thanks to which this material has a cellular structure.
In terms of home insulation and water absorption, this material is superior to expanded polystyrene foam.
Important! This material also stands out for its greater strength and lower vapor permeability.
It is precisely because of the properties of this material that it is used to insulate a house from the outside, although the disadvantages of it and the foam version are exactly the same.
Example of extruded polystyrene foam
Stone (so-called basalt) wool
The third most popular type of building material is basalt wool.
The design of the slab hints at reduced thermal conductivity. The reason for this is the structure - it is fibrous and has a low density. Such material, interestingly, is not exposed to fire or decay. Interestingly, it is considered “breathable,” which means it allows air to pass in or out, preventing the appearance of fungus.
Example of stone wool
Important! This wool has a “relative” in the form of glass wool, but it is used less often as insulation.
Methods of wall insulation
Experts identify three main options for insulating walls outside.
The first is called a “wet facade”. The insulation is attached to the outer wall, then plastered.
Photo: Instagram fasad.ug
The second is the construction of walls consisting of three non-ventilated layers. The insulation is fixed on the first of them, then a small air cushion is left and another brick-thick wall is built.
Photo: Instagram encon.co.uk
The third is ventilated facades. A wind barrier is attached to the insulation, and siding or other decorative material is placed on top.
Photo: Instagram ziasfacadesystem
Other external insulation materials
Today, in addition to the above options, you can find alternative insulation options in construction stores:
- polyurethane foam;
- "Teplover"
- ecowool;
- liquid ceramic insulation.
Polyurethane foam
This material is a familiar polyurethane foam. As a rule, it is used to seal cracks during the construction of building structures.
Polyurethane foam (another name is PPU) is a good option when the task is to insulate a house and create a seamless surface.
It is worth noting that it is better not to install such material yourself - this should be entrusted to specialists who will carry out high-quality work on insulating the outside of the house using special equipment.
Important! Previously, only professional equipment was used to apply such material, but now it can be bought in the form of an aerosol that anyone can handle.
pros
- absence of seams and joints - fastening such material allows you to achieve maximum integrity of the insulating structure, therefore the chance of seams and joints appearing is minimal;
- versatility - polyurethane foam “sticks” well to almost any material, from wood to concrete;
- long service life - deterioration of properties of polyurethane foam appears at least after a quarter of a century;
- self-extinguishing - this material has a very low flammability rate, which means it will not be able to maintain combustion.
Minuses
- poor holding power.
Polyurethane foam is a fairly popular material used as insulation.
Ecowool
Quite an interesting material that can be used for insulation. It stands out for its naturalness: 80% - cellulose, 20% - boric acid/borax.
Ecowool is applied in three different ways:
- Manual.
- Mechanized.
- Wet styling.
In the first case, such cotton wool is applied using improvised tools. The second option involves the use of a blow molding unit. The third requires the application of an adhesive binder and cellulose wool using a special nozzle and a water supply unit.
pros
- environmental friendliness - the material will not harm health because it is natural;
- ease of preparation - you just need to stir everything and the material is ready for application;
- ease of installation - even a beginner in the field of repair and construction can cope with the application.
Minuses
- not detected.
Ecowool - natural high-quality material for wall coverings
Teplover
It is considered a relatively new material. It is a plaster made on the basis of minerals such as vermiculite and perlite. The mixture stands out because, in addition to thermal insulation properties, it also has sound insulation properties.
This material has advantages and disadvantages that are worth considering.
pros
- durability;
- ease of preparation;
- high reliability;
- allows the wall to “breathe”;
- non-flammability - can withstand temperatures of more than 1000 degrees Celsius.
Minuses
- price – such material is quite expensive;
- complex application technology.
Important! It may be difficult to insulate a house with such a mixture on your own, so insulation with Teplover should be done by professionals with special equipment.
Heatover is a modern development that will satisfy the needs of most buyers
Liquid ceramic insulation
This type of thermal insulation can be used not only inside, but also outside the house. Externally, it is a liquid suspension (in some cases even a paste), resembling acrylic paint in consistency and appearance.
The basis of “liquid insulation” is a water-acrylic mixture. It is not only distributed evenly, but also spreads in a thin elastic layer over the entire surface.
The most important component of this suspension is ceramic spherical microgranules, the voids of which are filled with vacuum. It is these granules that provide not only heat preservation, but also a reduction in heat loss.
Important! Liquid insulation is somewhat reminiscent of a thermos in its functions.
In addition to granules, the water-alkyd mixture includes silicone, rubber and other additives. They will strengthen the insulation and reflect IR and UV radiation.
Let's consider the pros and cons of the material.
pros
- unable to burn;
- relatively environmentally friendly material;
- It is quite easy to apply due to the liquid form of the insulation.
Minuses
- The cost of this type of insulation is quite high.
Liquid insulation is the most technologically advanced and fresh variation of thermal insulation
Insulation - what you need to know about it
Which insulation for the outside walls of a house to use is not always an easy choice
To buy insulation for walls inside the house, you need to carefully study the issue and know about the features of such materials. The owner of a newly built house is extremely rarely interested in such issues - there are reasons for this.
The bottom line is that modern structures are built in accordance with modern technologies. However, owners of old foundations can also radically improve their conditions: the problem of saving energy is easily solved - the technology of insulating the external walls of houses will help with this. This works even when through holes appear in the walls.
What else can you say about the choice of insulation:
- It is difficult to buy insulation for walls inside a house, if only because there is no universal material. There is a certain factor - heat calculation of the outer wall of a residential building;
- Therefore, when selecting material, it is necessary to take this factor into account. Also, in order for the walls of a house to have reliable, high-quality thermal insulation, it is necessary to clearly understand what requirements the material must meet.
Insulation characteristics are an aspect that should not be ignored when choosing
It's time to answer an important question - what characteristics should high-quality insulation have?
The first thing you need to pay attention to is the degree of insulation. Without a doubt, this factor is important and it does not in all cases depend on how thick the material is; Certain insulation materials are small in size but retain heat better than other solutions.
This is due to both the reflective qualities of the products and their density - due to all this, a thermos effect is created, the house retains heat; We must not forget about lightness. The weight of the insulation is extremely important, especially for those structures that are old and built from materials of low strength. For houses on an old foundation, this point is also very relevant.
Cost - of course, there is no need to purchase the cheapest insulation materials. As a rule, such materials cannot boast of high quality. But there is no point in overpaying. The formation of value occurs like this - brand awareness plays a role here (the payment goes both for the material and for its name). The optimal solution is to find a middle ground. But this is not as easy as it may seem initially; Good insulation is resistant to temperature changes. If we talk about the facade, then there can be both external and internal temperature changes. From this we can draw a simple conclusion: under the influence of these vibrations, the insulation should not deform or lose its shape; Durability level - certain insulation materials may lose their insulation properties over time. If this happens, the insulation for the walls inside the house is unlikely to be able to fully function further. There is a way out of this situation, it is very simple: the facade will have to be changed
But, this procedure is not only time-consuming, but also significantly expensive; Before you buy insulation for walls - inside or outside the house, you need to pay attention to vapor permeability. Since temperature changes are observed frequently, condensation often occurs under the insulating layer
It has to evaporate somewhere - under ideal conditions. If there is no evaporation, both the building materials from which the walls are constructed and the finishing panels will suffer; There must be resistance to moisture - insulation for the walls of a house is almost always subject to one or another natural influence. Moisture is a real threat to almost any material. Therefore, the higher the water permeability of the insulation, the better for everyone.
The material must be resistant to moisture, or additional protection will have to be made
These criteria are not all that need to be taken into account when purchasing. But if all the recommendations are followed, the likelihood of making the right choice increases significantly.
External walls of houses are insulated using technologies that can be divided into two large groups:
- Wet method of applying the material;
- Dry application method.
People often wonder which method to choose. This question is important, the answer to it depends on various factors: the characteristic features of the house’s design play a role, as well as the climatic conditions of the region.
How to properly insulate the outside walls of a house so that the result is excellent and the savings in coolant increases many times even in the first heating season? More on this below.
About the choice of insulation - just a complicated matter
You need to choose insulation depending on two factors: what the wall is made of and what the finishing will be.
Let's look at the main options below.
Brick walls
Wet facade
Clause 8.5 of SP 23-101-2004 says the following: vapor permeability of the inner layer (insulation) < vapor permeability of the outer layer (finishing). In other words, the insulation has one task - to help the walls ventilate moisture.
The best option in this case would be mineral wool. The reason for this choice is high vapor permeability. An alternative option would be polystyrene foam + a layer of plaster, since brick walls are not very good at removing moisture.
Facing brick
If for the finishing treatment of brick walls the choice fell on facing brick, then you can use expanded polystyrene in its two variations and stone wool.
Important! If stone wool is used, then you need to create a small but ventilated air gap. In this case, the water will evaporate, and the walls will not get wet.
An example of laying thermal insulation on a brick wall with facing brick finishing
Ventilated facade
If you don’t use facing bricks for cladding a brick wall and don’t make a wet facade, then you should take a closer look at the advice of professionals. They may suggest using porcelain stoneware in the form of large slabs. You can also use wall panels as a finishing treatment. In addition, it is often suggested to use stone wool as insulation.
An example of laying thermal insulation on a brick wall with a ventilated façade finish
The use of mineral wool insulation for thermal insulation of house facades
According to all the main characteristics, mineral wool for wall insulation is the most preferred material, presented on the market in a wide variety: in rolls and slabs, of different thicknesses and densities, etc. Depending on the source raw materials, thermal insulation materials are:
- basalt (more often they are called mineral wool) and are made from dolomite or basalt rocks;
- glass wool – characterized by the presence of molten glass in its composition;
- slag wool - waste from the mining and metallurgical industries is used for its production.
If you plan to insulate the outside of the house with mineral wool for siding or other panels, then it is better to give preference to basalt products that have the highest performance characteristics.
For wooden houses, this is practically the only possible insulation option, since the material is vapor permeable and fireproof.
And, most importantly, it can be used both for the construction of a suspended ventilated structure and for the installation of a “wet” facade.
Among the main advantages of the material are:
- excellent vapor permeability;
- fire resistance and fire safety;
- environmental friendliness;
- moisture resistance, but may lose their performance characteristics with prolonged exposure to water and, as a result, getting wet;
- resistance to many chemical compounds;
- do not serve as a favorable “soil” for various microorganisms, including mold, fungi, etc.;
- low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- are an excellent soundproofing material;
- long service life, depending on the type of product and operating conditions from 25 to 50 years.
Thermal insulation materials made from mineral wool have virtually no disadvantages, except for the relatively high price of the products. But when choosing mineral wool insulation for the facade of a house, you should pay attention to rigid or semi-rigid products intended for vertical use.
They have better resistance to caking and shrinkage. They are produced in the form of slabs, as well as in rolls, which are presented on the market in different sizes, which allows you to ideally select the product depending on the chosen installation method and the area of the building.
Walls made of aerated concrete blocks
Wet facade
According to paragraph 8.5 of SP 23-101-2004 and taking into account the fact that the wall is made not of brick, but of aerated concrete blocks, it would be better to use stone wool. If the premises are well ventilated from the inside, then polystyrene foam can be installed.
Facing brick
When a wet facade is not satisfactory, you can choose another option - facing bricks. Then not only stone wool, but also polystyrene foam can act as insulation.
Important! If you choose stone wool, then you simply need to install a ventilation gap between the facing brick and the insulation so that the moisture evaporates.
An example of laying thermal insulation on an aerated concrete wall with facing brick finishing
Insulation of facades: main methods and types
To insulate a house from the outside, you can use not only a variety of materials, but also choose a wet or dry method.
The first option includes the “wet facade” technology, familiar to many, in which insulation is carried out using polystyrene foam or mineral wool, followed by the application of a plaster layer.
This type is especially common among owners of apartment buildings who are trying to improve the microclimate in their apartment in this way. But in this case they are not always able to achieve the desired result, since this method of insulation is effective if the entire structure is thermally insulated.
It is also common in private housing construction, as well as in the reconstruction of panel, brick and other buildings that initially do not have high thermal insulation characteristics.
The wet method of insulating the external walls of a house also includes the use of so-called “warm” plasters, which are a regular mixture with the addition of perlite.
But taking into account the fact that the layer of plaster cannot be too large, this method is effective if there is a need to slightly improve the thermal conductivity of a house located in regions with a mild climate and short winters.
But as an option it can be used as an outer layer of finishing for “wet facades” - in this case it is possible to use thinner insulation for the walls of the house outside under plaster, the cost of which is lower.
The “dry” method of insulation is most common in multi-layer systems of ventilated facades, and the main advantage of this type, in addition to the complete absence of wet processes, can be considered the fact that work can be carried out at any time of the year.
The only exceptions are rainy or windy days, as well as the season of heavy snowfall.
At the same time, for “wet” facades, the restriction on work occurs when the mercury column approaches zero.
Insulation of walls. Practical advice. Video:
Voting: the best external insulation for walls
What external wall insulation would you choose or recommend?
KNAUF Therm HOUSE
9.09 % ( 2 )
Knauf Therm Wall Pro
4.55 % ( 1 )
Knauf Therm Facade PRO
13.64 % ( 3 )
Carbon Eco TB
9.09 % ( 2 )
Ursa XPS-N-III-L G4
0.00 % ( 0 )
TechnoNIKOL Technoplex
4.55 % ( 1 )
Penoplex Wall
18.18 % ( 4 )
Paroc Extra
4.55 % ( 1 )
TechnoNIKOL Technovent Optima
9.09 % ( 2 )
TechnoNIKOL TechnoFas Cottage
9.09 % ( 2 )
Rockwool Facade Butts
18.18 % ( 4 )
How can you insulate a structure from the outside?
There are several methods, because there are even dozens of materials for thermal insulation work. Some of them cannot be implemented without the involvement of specialists, while others allow you to carry out all the work on saving heat outside the house with your own hands. Let's consider the second option.
Insulation using the well method
Suitable for using bulk type insulation and thermal insulation boards. The essence of the work is simple: first, a box or load-bearing walls are built. Then, with an indentation of 15-30 cm, everything is lined with an additional row of bricks. At the same time, the thickness of the second line is half a brick. Load-bearing and decorative (external) walls are created. The space between them (emptiness) is called a well.
The step from one wall to another can be adjusted using anchors or a special reinforcing mesh. It acts as a covering for the section of the well and strengthens the outer wall. This option for protecting the house structure from the outside is good because the dew point moves inside the decorative wall. Moisture accumulates on a cold wall, but thanks to the space with circulating air inside, it begins to dry out quickly.
Still, air inside alone is not enough, so the space is filled with insulating material. What is the best way to insulate the walls of a house? EPPS, polyurethane foam, mineral wool, expanded clay; ecowool, polystyrene foam.
Important! If you work with slab products, then they must be mounted exclusively on the surface of the internal main wall.
Creating a ventilated façade
The outside of the house can be made not only warm, but also beautiful. For example, if you want to use siding, lining, imitation timber, panels of various types, planks for cladding, then a ventilated facade is the best way to properly insulate a house.
In some ways, the technology resembles well technology. But there are significant differences. The essence of the work: metal guides are installed on the wall surface in a vertical position. The fastening pitch is selected depending on the width of the external insulation. The insulating material will be attached to the created space. In this case, fixation can be done with glue or dowels. It is important to lay the heat insulator tightly so that cold bridges do not form.
The next stage is to cover the warm walls with a vapor-waterproofing membrane. This can be a simple polyethylene film. The film is attached with an overlap. All that remains is to hide the insulating cake with the selected decorative material. And thanks to the ventilation gap created between the insulation and the cladding, moisture will quickly evaporate from the surface.
Most often, the technology of a ventilated facade from the outside is carried out using mineral wool.
Wet facade
The most popular insulation scheme among beginners. The peculiarity of the technology is that the problem of dew falls is solved by itself, and the arrangement does not require a lot of money. The essence of the work is this: insulation boards are fixed to the frame of a building in a private house. Penoplex, mineral wool or expanded polystyrene are most often used. Before work, the walls are leveled, puttied and all cracks are eliminated.
To hold the first row of slabs around the perimeter, a starting strip is fixed. After which each mat or slab is fixed in its place. The first row begins to be laid out from the bottom from the corner. The insulation is fixed with 5 dowels with umbrellas (at each corner and in the center). The next row is also fixed, but offset so that the seams do not intersect.
When the external thermal insulation is completed and all the walls are finished with insulation, an adhesive solution is applied on top and a reinforcing mesh is embedded. On top of the mesh you need another layer of glue. Now the surface is ready for decorative finishing. What exactly it will be, everyone decides for themselves. This is ordinary plaster with subsequent painting, bark beetle, fur coat and similar options. This insulating cake has no voids inside, so dew will not fall out at all.
Important! If you insulate the walls with polystyrene from the outside, it is important not to leave it unprotected for a long time in direct exposure to sunlight.
This completes the work. Thanks to such measures, you can reduce utility costs by half. Yes, at first you need to spend time, effort and money, but the efforts will pay off after a few months. In summer the room will be cool, in winter it will be warm and comfortable. Having considered how to insulate the house from the outside and with what, you can get to work.
Why is it better to insulate walls from the outside rather than from the inside?
When the insulation layer is located indoors, the outer wall experiences negative environmental influences - temperature changes, frost, ultraviolet radiation, precipitation. All this gradually destroys the material. Another serious point that must be taken into account when installing internal insulation is that the dew point penetrates into the thickness of the wall. Consequently, in cold weather condensation will constantly collect in it.
Damp walls are an excellent breeding ground for mold and fungi, which will be almost impossible to get rid of. Not to mention the fact that when installing insulation internally, you will have to sacrifice living space.
All these negative aspects are irrelevant if you insulate the walls of the house from the outside. You will save useful space in the premises, and the walls will receive additional protection from moisture, sun and extreme temperatures. At the same time, the quality of thermal insulation will be no worse.
Recommendation! When solving the issue of insulating a house, it is necessary to first consider the external installation of the material. And only in the absence of such a possibility, work is carried out indoors. It is important to perform high-quality vapor barrier.
Features of wall insulation outside the house - ventilated facade
Mineral wool is used for the ventilated façade. In simple words without using construction terms, a frame is assembled on the wall from a metal profile with cells the size of mineral, fiberglass or basalt slabs, or the same profiles are attached in a line from the bottom to the top of the building, between which insulation is laid. Afterwards it is covered with a special hydro- and vapor barrier film. The cladding is made with ceramic-granite tiles (usually 50x50 cm), which are fixed to the same guides using special metal clamps called “crabs”.
A ventilated facade is not only insulation, but also an aesthetic decoration of building facades
In this way, the developer achieves a solution to several problems at once - insulation, vapor barrier and finishing.
What is the best way to insulate walls outside?
Each type of modern insulation for exterior walls of a house has its own characteristics and price range. But their main differences are:
- low thermal conductivity coefficient;
- minimum values of water absorption and vapor permeability;
- the ability to regulate the indoor microclimate;
- high sound absorption rates;
- environmental cleanliness;
- fire resistance and fire safety;
- resistance to chemical attack;
Comparative table of thermal conductivity of building materials - resistance to biological and mechanical influences (molds, insects, rodents);
- strength and durability;
- elasticity and lack of shrinkage;
- low weight;
- possibility of installation without seams, joints, voids;
- ability to fill complex and hard-to-reach areas;
- ease of installation.
It is also important to take into account how the consumer prefers to install insulation for the walls of the house outside. Nowadays you can find enough videos showing the possibility of doing the work yourself (as well as other manuals).
The optimal insulation for walls is selected taking into account the material of construction.
Water absorption and vapor permeability are taken into account to ensure maximum protection of the room from moisture and are selected taking into account the climate and depending on the installation method. Thermal conductivity is used to calculate the required thickness of thermal insulation material.
The most commonly used types of insulation are:
- expanded polystyrene (foam);
- extruded polystyrene foam (eps, penoplex);
- polyurethane foam;
- mineral wool;
- basalt insulation;
- liquid thermal insulation.
Materials for external wall insulation
Expanded polystyrene (foam)
Polystyrene foam (expanded polystyrene) is one of the modern polymer insulation materials for house walls and is used in this capacity in almost all areas of the construction industry: civil and industrial.
First of all, this material is characterized by low thermal conductivity (from 0.037 to 0.052 W/m*K, depending on density) and water absorption, resistance to biological and chemical influences, and high sound insulation and windproof properties. It belongs to the group of environmentally friendly substances and is quite durable: its service life exceeds 50 years.
Fact! A layer of foam plastic 50 mm thick is equivalent to a wall of one and a half bricks in terms of heat retention.
Among its other advantages are flexibility and light weight. This helps reduce the cost of delivery and installation, ease of work, and reduces the load on the walls, which, in turn, eliminates the need for additional strengthening of the foundation.
The disadvantage of polystyrene foam is its flammability, however, the low price makes it possible to insulate all the outside walls of the house with foam plastic.
Extruded polystyrene foam (eps, penoplex)
Extruded polystyrene foam (penoplex) is one of the latest generation of thermal insulation materials. In its production, graphite is used in the form of nanoparticles, which increases the strength and energy saving of the product.
Insulation of walls with penoplex followed by cladding with siding
The thermal conductivity coefficient of penoplex insulation ranges from 0.029 to 0.031 W/m*K. It is resistant to mold, chemicals, insects and rodents, and is an excellent sound insulator.
Thanks to this, it is possible to use penoplex as insulation outside: for the walls of wooden houses and other buildings, and inside: thermal insulation of ceilings (especially when installing “warm” floors), basements, balconies and loggias.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is a type of plastic with a cellular foam structure. The mass of cells filled with air is 90% of the total weight of the product. Due to this, the thermal conductivity coefficient of polyurethane foam is one of the lowest - from 0.023 to 0.041 W/m*K.
Liquid polyurethane foam creates an airtight coating with excellent vapor and waterproofing.
Polyurethane foam has a high level of adhesion to all types of surfaces: concrete, brick, wood, metal - due to which an airtight coating is created with a guarantee of excellent vapor and waterproofing.
A seamless application method (using a compressor and a hose) and high elasticity make polyurethane foam an indispensable material for blown-in thermal insulation when insulating the outside walls of buildings of complex shapes and frame houses. Insulation for external walls using the blow-in method can be applied at temperatures up to 100ºС, the service life is up to 30 years.
Liquid polyurethane foam can be used as blow-in insulation between the building wall and the cladding.
The only disadvantage of the material is its high cost and the need to use expensive equipment for installation.
Mineral wool (basalt insulation, stone wool, glass wool)
Mineral wool is a product of processing slag (waste from the metallurgical industry) or rocks: basalt and dolomite. It is distinguished by strength, non-flammability, durability, environmental friendliness, elasticity, high degree of sound absorption, ease of installation and low cost. The thermal conductivity of this material is in the range of 0.034 – 0.037 W/m*K.
Mineral wool is characterized by fire resistance, environmental friendliness, a high degree of sound absorption and low cost.
For insulation work, mineral wool is used in the form of basalt slabs or in rolls with a wide range of sizes. Mineral wool is used as insulation for the outside walls of a house. The dimensions of the produced slabs can be as follows:
- 1000 x 600 x 50 mm;
- 7000 x 1200 x 50 mm;
- 9000 x 1200 x 50 mm;
- 10000 x 1200 x 50 mm;
- 10000 x 1200 x 100 mm.
Expanded polystyrene boards may have joint grooves for ease of installation
Basalt insulation is used in buildings for any purpose, especially for insulation in dachas, wooden houses and buildings made of timber, brick or foam blocks. It is possible to work with this material at temperatures ranging from -60ºС to +220ºС, which is definitely convenient when installing on walls outside. Insulation in dachas, houses made of wood, brick or foam blocks, garages, warehouses and other buildings - this is an incomplete list of possibilities for using mineral thermal insulation.
It is most preferable to use mineral wool or basalt slabs when installing insulation for the walls of a house outside under the siding.
It is most preferable to use mineral wool to insulate a house from the outside, followed by siding.
It is also popular to use mineral wool (along with polyurethane foam) to create blow-in insulation. With this method, using a compressor unit, the material is blown between the wall of the house and the finishing facade, which also serves as formwork.
Liquid thermal insulation
Liquid thermal insulation materials can be called new generation insulation materials. They can be used for thermal insulation of metal parts (pipes or frames) and as insulation for houses made of foam blocks. On the outside, on the walls, these ceramic multi-component substances look like acrylic paint.
However, they differ from paint in the content of vacuumized voids (up to 80%), due to which they acquire the properties of a heat insulator.
Liquid insulation is similar to acrylic paint
Interesting! Liquid insulation has a record low thermal conductivity coefficient (from 0.0011 to 0.0015 W/m*K). For comparison, the thermal conductivity coefficient of vacuum is 0.
With a liquid consistency, these materials do not require professional skills and complex equipment for application to any surface: concrete, brick, metal, wood. They are applied using painting tools: brushes, rollers, airless spray guns - and fill all voids and crevices.
After 6 hours of drying, a solid, highly mechanically resistant coating is formed.
Fixation of sheets of polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene is carried out with special fastenings of the “mushroom” type.
Due to their low thermal conductivity, liquid insulation for the walls of a house helps reduce heat loss, even if applied externally in a thin layer. They protect the surface from weather influences (operating temperature range - from -60 to +260°C), solar radiation and precipitation, and metal parts from corrosion.
Interesting! Water absorption of most liquid insulation materials within 24 hours does not exceed 0.4% by weight.
Coating with liquid insulation is one of the effective ways to prevent the formation of condensation and protect an industrial or residential premises from freezing and the development of all types of mold fungi.
Calculation of insulation for house walls: convenient online calculators
It is not difficult to calculate the required dimensions of the slabs according to the length and width of the wall. A much bigger problem here is the calculation of the required thickness, which depends on many different parameters, including the region in which the residential building is located. That is why we suggest you use our online calculators, which will perform all the calculations themselves.
Online calculator for calculating the thickness of insulation of the walls of a wooden house
Online calculator for calculating the thickness of wall insulation with Penoplex
Scheme map for determining the required value of heat transfer resistance
Where to buy insulation for outside walls of a house
You can purchase such material both online and at any construction market. Here the question is a little different - the cost can vary significantly. Usually, when purchasing thermal insulation in online stores, especially in large quantities, you can save a decent amount. This happens because the online seller does not need to pay salaries to subordinates and spend money on renting premises for a retail outlet. This means that purchases are obtained with significant benefits. The same applies to the price of insulation for the walls of the house inside.
The range of insulation in construction markets is quite wide.
Insulation for outside walls of a house: price according to online catalogs
Let's try to summarize the information on prices for various heat insulators that we were able to find on the Internet.
| Material | Dimensions, mm | Cost, rub./piece |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 1200x600x30 | 150 |
| Mineral plate | 1200x600x40 | 100 |
| Styrofoam | 1200x500x20 | 15-20 |
| Mineral wool (roll) | 8200x120x50 | 100 |
Separately, you can mention a new product - sprayed aerosol insulation “POLINOR” at a price of 500 rubles per cylinder (1 kg).
When insulating walls with mineral or glass wool, it is better to use a respirator
Calculation of insulation thickness
How to determine how thick a layer of insulation is required to achieve the optimal level of thermal insulation for a home? This issue actually requires increased attention, because a mistake of just a couple of centimeters can turn into problems that will require serious investment to correct.
The thickness of the insulation is calculated taking into account the quality of the material and its technical characteristics. Of particular importance are:
- heat transfer resistance coefficient;
- thermal conductivity.
These indicators characterize the amount of heat passing through m² of material surface.
Sometimes it is necessary to lay insulation in several layers. In this case, the overall indicators of the “pie” will be the sum of the individual values of each layer. It is also necessary to take into account what material the walls themselves are made of.
The climatic characteristics of the region are also included in the calculations. It is clear that the insulation of the exterior walls of a house will be different for the north of Siberia and the Krasnodar Territory.
Calculations are carried out on the basis of standard parameters given in SNiP 02/23/2003 “Thermal protection of buildings” and 01/23/99 “Climatology”. The first document contains background information regarding the heat transfer coefficients of building envelopes (R0), and from the second you can find out the temperature values and the duration of the heating season in the region.
The next step is to determine the parameters of the building's structural elements. You need to find out what materials the walls, floor, and attic ceiling are made of. For example, a house on stilts may have a three-layer floor:
- the lower part of the support beams is hemmed with boards;
- then a layer of insulation is installed;
- Boards are attached on top of the beams, on which the finished floor is then laid.
In this case, it will be necessary to take into account the thermal conductivity (λ1) of each layer.
Then the thermal resistance of the main building material (R1) should be calculated taking into account its thickness (δ1) in meters.
The calculation is performed using the formula:
R1 = δ1 / λ1.
Then you need to find out by what amount you want to increase the thermal resistance (R2) of the structure due to insulation:
R2 = R0 - R1.
Now you can proceed directly to determining the required insulation thickness (δ2). To do this, you need to multiply the resulting value of the missing resistance R2 by the value of thermal conductivity λ2 of the material that you want to use for insulation:
δ2 = R2 * λ2.
The resulting value will be the thickness of the insulation in meters. All roundings of the calculated value are made upward.